Comparison of Biological, Pharmacological Characteristics, Indications, Contraindications, Efficacy, and Adverse Effects of Inactivated Whole-Virus COVID-19 Vaccines Sinopharm, CoronaVac, and Covaxin: An Observational Study
- PMID: 37112738
- PMCID: PMC10146574
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040826
Comparison of Biological, Pharmacological Characteristics, Indications, Contraindications, Efficacy, and Adverse Effects of Inactivated Whole-Virus COVID-19 Vaccines Sinopharm, CoronaVac, and Covaxin: An Observational Study
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is an emerging viral zoonotic illness that has developed a distinctive and threatening situation globally. Worldwide, many vaccines were introduced to fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. The present study aims to compare the bio-pharmacological characteristics, indications, contraindications, efficacy, and adverse effects of inactivated whole-virus COVID-19 vaccines, Sinopharm, CoronaVac, and Covaxin. Initially, 262 documents and 6 international organizations were selected. Finally, 41 articles, fact sheets, and international organizations were included. The data were recorded from the World Health Organization (WHO), Food and Drug Administration (FDA) USA, Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, and Scopus. The results demonstrated that these three inactivated whole-virus COVID-19 vaccines, Sinopharm, CoronaVac, and Covaxin, received emergency approval from the FDA/WHO, and all three of these vaccines are beneficial for the prevention of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Sinopharm vaccine has been recommended during pregnancy and for people of all age groups, and the CoronaVac and Covaxin vaccines are recommended for people over 18 years of age and older. These three vaccines have recommended intramuscular doses of 0.5 mL each, with a 3-4 week interval. These three vaccines can be stored in a refrigerator at +2 to +8 °C. The common adverse effects of these vaccines are pain at the injection site, redness, fatigue, headache, myalgias, general lethargy, body ache, arthralgia, nausea, chills, fever, and dizziness. The overall mean efficiency for the prevention of the COVID-19 disease is 73.78% for Sinopharm, 70.96% for CoronaVac, and 61.80% for Covaxin. In conclusion, all three inactivated whole-virus COVID-19 vaccines, Sinopharm, CoronaVac, and Covaxin, are beneficial for the prevention of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, evidence suggests that the overall impact of Sinopharm is slightly better than that of CoronaVac and Covaxin.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; adverse effects; pharmacology; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
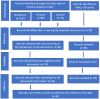
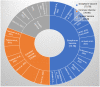
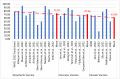
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 vaccines: comparison of biological, pharmacological characteristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1663-1669. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24877. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629336 Review.
-
Potential Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines on Iranian Healthcare Workers: Comparison of Four Available Vaccines in Tehran: A Retrospective Cross-sectional Study.Oman Med J. 2023 Mar 31;38(2):e486. doi: 10.5001/omj.2023.69. eCollection 2023 Mar. Oman Med J. 2023. PMID: 37168286 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Biological, Pharmacological Characteristics, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse Effects of JYNNEOS and ACAM2000 Monkeypox Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;10(11):1971. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111971. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36423066 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines.mSphere. 2022 Apr 27;7(2):e0091521. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00915-21. Epub 2022 Mar 14. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 35285250 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivated vaccine Covaxin/BBV152: A systematic review.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 9;13:863162. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.863162. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36016940 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the association between vaccine attitude, vaccine conspiracies and self-reported side effects following COVID-19 vaccination among nurses and physicians in Jordan.Vaccine X. 2023 Nov 8;15:100405. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2023.100405. eCollection 2023 Dec. Vaccine X. 2023. PMID: 38161986 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the adverse events of Oxford-AstraZeneca, Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and Johnson and Johnson COVID-19 vaccination on Guillain-Barré Syndrome.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 13;14(1):18767. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66999-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39138276 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Pandemic Era: Recent Advances and Efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Against Emerging Variants of Concern.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Apr 17;13(4):424. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13040424. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40333293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Vaccines Effectiveness and Safety in Trinidad and Tobago: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 10;13(1):135. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010135. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 39858903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with COVID-19 among hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory infections in Serbia, 2022-2023: A test negative case-control study.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 18;19(3):e0299210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299210. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38498428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 25 March 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2. Transmission. [(accessed on 23 January 2023)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/sars-co.... - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Getting the COVID-19 Vaccine. [(accessed on 23 January 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/getting-the-covid-1....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

