Examining the Impact of Key Factors on COVID-19 Vaccination Coverage in India: A PLS-SEM Approach
- PMID: 37112780
- PMCID: PMC10144197
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040868
Examining the Impact of Key Factors on COVID-19 Vaccination Coverage in India: A PLS-SEM Approach
Abstract
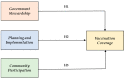
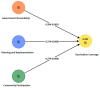
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, numerous factors determined the performance of COVID-19 vaccination coverage. The purpose of this study is to examine the influence of factors such as government stewardship, planning and implementation, and community participation on COVID-19 vaccination coverage. This study applied partial least square structured equation modeling (PLS-SEM) by analyzing 187 responses from the stakeholders involved in vaccination programs in four select states of India. This study empirically validates a framework for improving vaccination coverage by confirming the significant impact of planning and implementation on vaccination coverage followed by government stewardship and community participation. Additionally, this study highlights the individual impact of each factor on vaccination coverage. Based on the findings, strategic recommendations were proposed that can be utilized for formulating policy-level actions to facilitate the vaccination program.
Keywords: COVID-19; India; community participation; government stewardship; partial least square; vaccination coverage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting intentions to get the COVID-19 vaccine in India: An integration of theory of planned behaviour and health belief model.Int J Health Plann Manage. 2023 Jan;38(1):214-238. doi: 10.1002/hpm.3582. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2023. PMID: 36164891 Free PMC article.
-
The whole-of-society approach of mass COVID-19 vaccination in China: a qualitative study.Health Res Policy Syst. 2022 Dec 30;20(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12961-022-00947-7. Health Res Policy Syst. 2022. PMID: 36585666 Free PMC article.
-
Using a low-cost, real-time electronic immunization registry in Pakistan to demonstrate utility of data for immunization programs and evidence-based decision making to achieve SDG-3: Insights from analysis of Big Data on vaccines.Int J Med Inform. 2021 May;149:104413. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2021.104413. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Int J Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 33652259
-
The impact of COVID-19 and catch-up strategies on routine childhood vaccine coverage trends in Latin America: A systematic literature review and database analysis.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(6):2102353. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2102353. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 36084255 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinating a billion people against COVID-19: India's quest for systems leadership in exceptional times.Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). 2021 Nov 19;ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). doi: 10.1108/LHS-05-2021-0045. Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). 2021. PMID: 34787981 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunological orchestration and dysregulation in COVID-19 pneumonia: from viral pathogenesis to precision therapeutics in the post-pandemic era.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025 Aug 18. doi: 10.1007/s12223-025-01315-y. Online ahead of print. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025. PMID: 40826253 Review.
-
Overall leukocyte levels link risk factors to Von Willebrand factor and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in stroke thrombi: a Structural Equation Modeling analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1515596. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1515596. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40625905 Free PMC article.
-
Sustaining the mobile medical units to bring equity in healthcare: a PLS-SEM approach.Int J Equity Health. 2024 Sep 2;23(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12939-024-02260-x. Int J Equity Health. 2024. PMID: 39218941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—8 February 2022. 2022. [(accessed on 8 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources