The Broad-Spectrum Endolysin LySP2 Improves Chick Survival after Salmonella Pullorum Infection
- PMID: 37112818
- PMCID: PMC10142873
- DOI: 10.3390/v15040836
The Broad-Spectrum Endolysin LySP2 Improves Chick Survival after Salmonella Pullorum Infection
Abstract
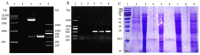
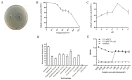
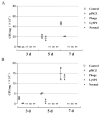
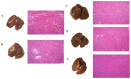
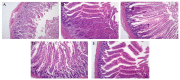
Salmonella pullorum causes typical "Bacillary White Diarrhea" and loss of appetite in chicks, which leads to the death of chicks in severe cases; thus, it is still a critical issue in China. Antibiotics are conventional medicines used for Salmonella infections; however, due to the extensive long-term use and even abuse of antibiotics, drug resistance becomes increasingly severe, making treating pullorum disease more difficult. Most of the endolysins are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. A virulent bacteriophage, YSP2, of Salmonella was isolated in a previous study. A Pichia pastoris expression strain that can express the Salmonella bacteriophage endolysin was constructed efficiently, and the Gram-negative bacteriophage endolysin, LySP2, was obtained in this study. Compared with the parental phage YSP2, which can only lyse Salmonella, LySP2 can lyse Salmonella and Escherichia. The survival rate of Salmonella-infected chicks treated with LySP2 can reach up to 70% and reduce Salmonella abundance in the liver and intestine. The treatment group showed that LySP2 significantly improved the health of infected chicks and alleviated organ damage caused by Salmonella infection. In this study, the Salmonella bacteriophage endolysin was expressed efficiently by Pichia pastoris, and the endolysin LySP2 showed good potential for the treatment of pullorum disease caused by Salmonella pullorum.
Keywords: Pichia pastoris; Salmonella pullorum; endolysin; expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

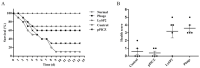
Similar articles
-
Isolation and identification of Salmonella pullorum bacteriophage YSP2 and its use as a therapy for chicken diarrhea.Virus Genes. 2018 Jun;54(3):446-456. doi: 10.1007/s11262-018-1549-0. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Virus Genes. 2018. PMID: 29564689 Clinical Trial.
-
Salmonella phage CKT1 significantly relieves the body weight loss of chicks by normalizing the abnormal intestinal microbiome caused by hypervirulent Salmonella Pullorum.Poult Sci. 2022 Mar;101(3):101668. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101668. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35063807 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of E. coli Nissle 1917 on chickens infected with Salmonella pullorum.Microb Pathog. 2022 Nov;172:105768. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105768. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36096456
-
Fowl typhoid and pullorum disease.Rev Sci Tech. 2000 Aug;19(2):405-24. doi: 10.20506/rst.19.2.1222. Rev Sci Tech. 2000. PMID: 10935271 Review.
-
Northeastern Conference on Avian Diseases from 1928-2021: 93 Years of Contributions to Organized Avian Medicine.Avian Dis. 2022 Mar;66(1):7-19. doi: 10.1637/aviandiseases-21-00074. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Avian Dis. 2022. PMID: 35092237 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparative guide to expression systems for phage lysin production.Essays Biochem. 2024 Dec 17;68(5):645-659. doi: 10.1042/EBC20240019. Essays Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39290148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage-derived proteins: Advancing food safety through biocontrol and detection of foodborne pathogens.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 Mar;24(2):e70124. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70124. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 39898971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding activity and specificity of tail fiber protein 35Q for Salmonella pullorum.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 25;15:1429504. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1429504. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38983624 Free PMC article.
-
Phage lysins for intestinal microbiome modulation: current challenges and enabling techniques.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2387144. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2387144. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39106212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limitation of the Lytic Effect of Bacteriophages on Salmonella and Other Enteric Bacterial Pathogens and Approaches to Overcome.Int J Microbiol. 2025 May 15;2025:5936070. doi: 10.1155/ijm/5936070. eCollection 2025. Int J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40405891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

