Validation of N Protein Antibodies to Diagnose Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Large Cohort of Healthcare Workers: Use of Roche Elecsys® Immunoassay in the S Protein Vaccination Era
- PMID: 37112910
- PMCID: PMC10146079
- DOI: 10.3390/v15040930
Validation of N Protein Antibodies to Diagnose Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Large Cohort of Healthcare Workers: Use of Roche Elecsys® Immunoassay in the S Protein Vaccination Era
Abstract
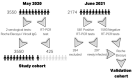
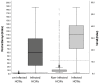
The aim of this study was to validate the detection of anti-nucleocapsid protein (N protein) antibodies for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in light of the fact that most COVID-19 vaccines use the spike (S) protein as the antigen. Here, 3550 healthcare workers (HCWs) were enrolled from May 2020 (when no S protein vaccines were available). We defined SARS-CoV-2 infection if HCWs were found to be positive by RT-PCR or found to be positive in at least two different serological immunoassays. Serum samples from Biobanc I3PT-CERCA were analyzed by Roche Elecsys® (N protein) and Vircell IgG (N and S proteins) immunoassays. Discordant samples were reanalyzed with other commercial immunoassays. Roche Elecsys® showed the positivity of 539 (15.2%) HCWs, 664 (18.7%) were found to be positive by Vircell IgG immunoassays, and 164 samples (4.6%) showed discrepant results. According to our SARS-CoV-2 infection criteria, 563 HCWs had SARS-CoV-2 infection. The Roche Elecsys® immunoassay has a sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and concordance with the presence of infection of 94.7%, 99.8%, 99.3%, and 0.96, respectively. Similar results were observed in a validation cohort of vaccinated HCWs. We conclude that the Roche Elecsys® SARS-CoV-2 N protein immunoassay demonstrated good performance in diagnosing previous SARS-CoV-2 infection in a large cohort of HCWs.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antibody response; infection; nucleocapsid protein; spike protein; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A performance comparison of two (electro) chemiluminescence immunoassays for detection and quantitation of serum anti-spike antibodies according to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and infections status.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28397. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28397. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36504019 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Roche SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antibody Test in Samples from Vaccinated Individuals.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0270921. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02709-21. Epub 2022 May 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35575594 Free PMC article.
-
Head-to-head comparison of two rapid high-throughput automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassays targeting total antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein and spike protein receptor binding domain.J Clin Virol. 2021 Apr;137:104784. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104784. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Clin Virol. 2021. PMID: 33711693 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting Waning Serological Response with Commercial Immunoassays: 18-Month Longitudinal Follow-up of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibodies.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0098622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00986-22. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35867423 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Elecsys Anti-SARS CoV-2 (Roche) and VIDAS Anti-SARS CoV-2 (Biomérieux) for SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Spike Protein Antibody Detection.EJIFCC. 2022 Aug 8;33(2):159-165. eCollection 2022 Aug. EJIFCC. 2022. PMID: 36313907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-specific antibody response associated with high clozapine doses in schizophrenia spectrum disorders.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 May 19;46:101016. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.101016. eCollection 2025 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40502531 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

