Impact of Borna Disease Virus Infection on the Transcriptome of Differentiated Neuronal Cells and Its Modulation by Antiviral Treatment
- PMID: 37112922
- PMCID: PMC10145824
- DOI: 10.3390/v15040942
Impact of Borna Disease Virus Infection on the Transcriptome of Differentiated Neuronal Cells and Its Modulation by Antiviral Treatment
Abstract
Borna disease virus (BoDV-1) is a highly neurotropic RNA virus that causes neurobehavioral disturbances such as abnormal social activities and memory impairment. Although impairments in the neural circuits caused by BoDV-1 infection induce these disturbances, the molecular basis remains unclear. Furthermore, it is unknown whether anti-BoDV-1 treatments can attenuate BoDV-1-mediated transcriptomic changes in neuronal cells. In this study, we investigated the effects of BoDV-1 infection on neuronal differentiation and the transcriptome of differentiated neuronal cells using persistently BoDV-1-infected cells. Although BoDV-1 infection did not have a detectable effect on intracellular neuronal differentiation processes, differentiated neuronal cells exhibited transcriptomic changes in differentiation-related genes. Some of these transcriptomic changes, such as the decrease in the expression of apoptosis-related genes, were recovered by anti-BoDV-1 treatment, while alterations in the expression of other genes remained after treatment. We further demonstrated that a decrease in cell viability induced by differentiation processes in BoDV-1-infected cells can be relieved with anti-BoDV-1 treatment. This study provides fundamental information regarding transcriptomic changes after BoDV-1 infection and the treatment in neuronal cells.
Keywords: Borna disease virus; antiviral; differentiation; gene expression; neuronal cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
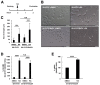
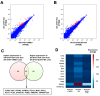
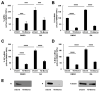


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

