Detection of IgA and IgG Antibodies against the Structural Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 in Breast Milk and Serum Samples Derived from Breastfeeding Mothers
- PMID: 37112946
- PMCID: PMC10144911
- DOI: 10.3390/v15040966
Detection of IgA and IgG Antibodies against the Structural Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 in Breast Milk and Serum Samples Derived from Breastfeeding Mothers
Abstract
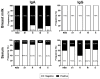
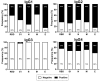
Background: COVID-19 vaccination or natural infection is associated with the development of immunity. The search of IgA and IgG antibodies against all the structural proteins (spike, nucleocapsid, membrane, and envelope) of SARS-CoV-2 in breastfeeding mothers is associated with immunity that can help the newborn avoid development of the infection. Methods: In this study, we analyzed 30 breastfeeding women that provided samples of breast milk and serum and evaluated the presence of IgA, total IgG, and subclasses against the structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2. Results: We reported a high seroprevalence to IgA (76.67-100%) and negativity to IgG against all analyzed proteins in breast milk. Seroprevalence in serum samples was around 10-36.67% to IgA and 23.3-60% to IgG. Finally, we detected the presence of the subclasses IgG1, IgG2, and IgG4 against all the structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2. Conclusions: This work provides evidence of the presence of IgA and IgG antibodies against the four structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 in breast milk and serum samples derived from breastfeeding women, which can confer immunity to the newborn.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgA; IgG; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; breastfeeding; structural proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgG and IgA in Serum and Milk with Different SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Breastfeeding Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Northern Spain.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 21;18(16):8831. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168831. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444579 Free PMC article.
-
Are SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Detectable in Human Milk After Vaccination Against COVID-19?J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022 Apr 30;11(4):126. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piac024. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022. PMID: 35394545 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG in human milk after vaccination is dependent on vaccine type and previous SARS-CoV-2 exposure: a longitudinal study.Genome Med. 2022 Apr 21;14(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01043-9. Genome Med. 2022. PMID: 35449030 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal vaccination as an additional approach to improve the protection of the nursling: Anti-infective properties of breast milk.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022 Aug 10;77:100093. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100093. eCollection 2022. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022. PMID: 35963149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and human milk: What is the evidence?Matern Child Nutr. 2020 Oct;16(4):e13032. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13032. Epub 2020 May 30. Matern Child Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32472745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in breast milk of women given one & two doses of COVID-19 vaccine.Indian J Med Res. 2024 Nov;160(5):501-505. doi: 10.25259/ijmr_964_23. Indian J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39737512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cascella M., Rajnik M., Aleem A., Dulebohn S.C., Di Napoli R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19) StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. [(accessed on 15 February 2023)]. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554776/ - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

