Streptomyces RNases - Function and impact on antibiotic synthesis
- PMID: 37113221
- PMCID: PMC10126417
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1096228
Streptomyces RNases - Function and impact on antibiotic synthesis
Abstract
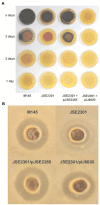
Streptomyces are soil dwelling bacteria that are notable for their ability to sporulate and to produce antibiotics and other secondary metabolites. Antibiotic biosynthesis is controlled by a variety of complex regulatory networks, involving activators, repressors, signaling molecules and other regulatory elements. One group of enzymes that affects antibiotic synthesis in Streptomyces is the ribonucleases. In this review, the function of five ribonucleases, RNase E, RNase J, polynucleotide phosphorylase, RNase III and oligoribonuclease, and their impact on antibiotic production will be discussed. Mechanisms for the effects of RNase action on antibiotic synthesis are proposed.
Keywords: RNA decay; RNA processing; Streptomyces; antibiotic; regulation; ribonuclease.
Copyright © 2023 Jones.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn S., Shin E. K., Yeom J. H., Lee K. (2008). Modulation of Escherichia coli RNase E activity by RraAS2, a Streptomyces coelicolor ortholog of RraA. Korean J. Microbiol. 44, 93–97.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

