Association between number of hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions and neurocognitive outcomes of acute carbon monoxide poisoning
- PMID: 37113603
- PMCID: PMC10127102
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1127978
Association between number of hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions and neurocognitive outcomes of acute carbon monoxide poisoning
Abstract
Background: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO2) is recommended for symptomatic patients within 24 h of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. Currently, there is no consensus on the number of HBO2 sessions within 24 h after arrival at the hospital. Therefore, we evaluated differences in the therapeutic effects according to the number of HBO2 sessions in acute CO poisoning.
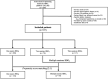
Methods: This cohort study included data collected from our CO poisoning registry and prospective cohorts between January 2006 and August 2021 in a single academic medical center in South Korea. Based on the number of HBO2 sessions performed within 24 h, we classified patients into one- and multiple- (two or three) session groups. We also compared mild (non-invasive mechanical ventilation) and severe (invasive mechanical ventilation) groups. CO-related neurocognitive outcomes were measured using the Global Deterioration Scale (GDS; stages: 1-7) combined with neurological impairment at 1 month after poisoning. We classified GDS stages as favorable (1-3 stages) and poor (4-7 stages) neurocognitive outcomes. Patients belonging to a favorable group based on GDS assessment, but with observable neurological impairment, were assigned to the poor outcome group. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to adjust for age, sex, and related variables to identify statistical differences between groups.
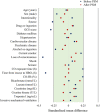
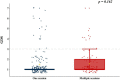
Results: We analyzed the data of 537 patients between ages 16 and 70 years treated with HBO2. After PSM, there was no significant difference in neurocognitive outcomes at 1 month among the two groups of patients (p = 0.869). Furthermore, there were no significant differences in neurocognitive outcomes between invasive mechanical ventilation and non-invasive mechanical ventilation patients in the three groups (p = 0.389 and p = 0.295).
Conclusion: There were no significant differences in the reduction of poor neurocognitive outcomes according to the number of HBO2 sessions implemented within 24 h of CO exposure.
Keywords: carbon monoxide poisoning; cognitive dysfunction; hyperbaric oxygen therapy; prognosis; session.
Copyright © 2023 Lee, Cha and Lim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Weaver LK. Carbon monoxide poisoning In: Moon RE, editor. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy indications. 14th ed. North Palm Beach, FL: Best Publishing Company; (2019). 81–104.
-
- Hampson NB, Weaver LK. Carbon monoxide poisoning: a new incidence for an old disease. Undersea Hyperb Med. (2007) 34:163–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

