Expression of Th1/2/17 Cytokines in CML with or without Pulmonary Bacterial and Fungal Coinfection
- PMID: 37114211
- PMCID: PMC10129429
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6318548
Expression of Th1/2/17 Cytokines in CML with or without Pulmonary Bacterial and Fungal Coinfection
Abstract
Background: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are the standard therapy for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). While their use greatly increases patient survival rates and can lead to normal life expectancy, bacterial infections in the lungs continue to play a significant role in determining patient outcomes.
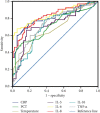
Methods: In this study, the medical records of 272 CML and 53 healthy adults were analyzed. Information on age, sex, body temperature, procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), and cytokine levels were collected from patients. Since the data belonged to a nonstate distribution, we used the Mann-Whitney U test to examine differences between groups. Cut-off values were analyzed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
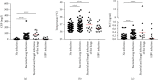
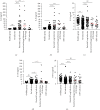
Results: No significant differences in the Th1/2/17 levels were observed in relation to TKI treatment. Further analysis showed that the levels of the interleukins IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-22, IL-12p70, IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-1β, interferon (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factors (TNF α and β) were higher in patients with pulmonary bacterial infections compared with uninfected patients. IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 levels in CML patients with bacterial and fungal coinfection were higher than those in patients without infection. The areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) were found to be 0.73 for IL-5, 0.84 for IL-6, 0.82 for IL-8, 0,71 for IL-10, and 0.84 for TNF-α. AUC values were higher for patients with pulmonary bacterial infection, especially IL-6 (AUC = 0.84, cut-off = 13.78 pg/ml) and IL-8 (AUC = 0.82, cut-off = 14.35 pg/ml), which were significantly better than those for CRP (AUC = 0.80, cut-off = 6.18 mg/l), PCT (AUC = 0.71, cut-off = 0.25 ng/ml), and body temperature (AUC = 0.68, cut-off = 36.8°C). In addition, according to the cut-off values, we found that 83.33% of patients with pulmonary bacterial infections had IL-6 ≥ 13.78 pg/ml, while when IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 levels simultaneously exceeded the cut-off values, the probability of pulmonary bacterial infection was 93.55%.
Conclusions: TKI treatment did not appear to affect cytokine expression in CML patients. However, CML patients with pulmonary bacterial infection had significantly higher levels of Th1/2/17 cytokines. In particular, abnormally elevated IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 levels were associated with a pulmonary bacterial infection in patients with CML.
Copyright © 2023 Xin Guan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

