Quantitative analysis of autophagy reveals the role of ATG9 and ATG2 in autophagosome formation
- PMID: 37115157
- PMCID: PMC10148237
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202210078
Quantitative analysis of autophagy reveals the role of ATG9 and ATG2 in autophagosome formation
Abstract
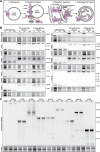
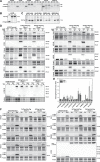
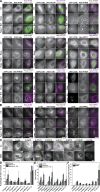
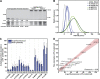
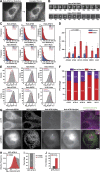
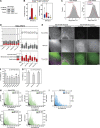
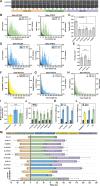
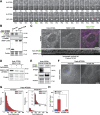
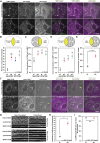
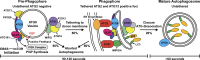
Autophagy is a catabolic pathway required for the recycling of cytoplasmic materials. To define the mechanisms underlying autophagy it is critical to quantitatively characterize the dynamic behavior of autophagy factors in living cells. Using a panel of cell lines expressing HaloTagged autophagy factors from their endogenous loci, we analyzed the abundance, single-molecule dynamics, and autophagosome association kinetics of autophagy proteins involved in autophagosome biogenesis. We demonstrate that autophagosome formation is inefficient and ATG2-mediated tethering to donor membranes is a key commitment step in autophagosome formation. Furthermore, our observations support the model that phagophores are initiated by the accumulation of autophagy factors on mobile ATG9 vesicles, and that the ULK1 complex and PI3-kinase form a positive feedback loop required for autophagosome formation. Finally, we demonstrate that the duration of autophagosome biogenesis is ∼110 s. In total, our work provides quantitative insight into autophagosome biogenesis and establishes an experimental framework to analyze autophagy in human cells.
© 2023 Broadbent et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures




Comment in
-
Toward a standard model for autophagosome biogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2023 Jul 3;222(7):e202304011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202304011. Epub 2023 Jun 5. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37273223 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

