The influence of 3D renal reconstruction on surgical planning for complex renal tumors: An interactive case-based survey
- PMID: 37115181
- PMCID: PMC10335884
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2022.0623
The influence of 3D renal reconstruction on surgical planning for complex renal tumors: An interactive case-based survey
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the role of three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction in preoperative planning for complex renal tumors.
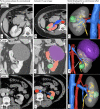
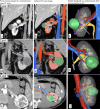
Materials and methods: A well-planned questionnaire was distributed among the attending urologists at an international meeting. The questionnaire inquired about demographic data, surgical experience, partial nephrectomy (PN) versus radical nephrectomy (RN), surgical approach, time of ischemia, probability of postoperative urine leakage and positive surgical margins after viewing computed tomography (CT) scans and their respective 3D models of six complex renal tumors. Following the CT scans, attendees were asked to view randomly selected reconstructions of the cases.
Results: One hundred expert urologists participated in the study; 61% were aged between 40 and 60 years. Most of them (74%) were consultants. The overall likelihood of PN after viewing the 3D reconstructions significantly increased (7.1±2.7 vs. 8.0±2.2, p<0.001), the probability of conversion to RN significantly decreased (4.3±2.8 vs. 3.2±2.5, p<0.001), and the likelihood of urine leakage and positive surgical margins significantly decreased (p<0.001). Preference for the open approach significantly decreased (21.2% vs. 12.1%, p<0.001), while selective clamping techniques significantly increased (p<0.001). After viewing the 3D models, low expected warm ischemia time and estimated blood loss were significantly preferred by the respondents (p<0.001). Surgical decision change was significantly associated with performance or participation in more than 20 PNs or RNs annually [3.25 (1.98-5.22) and 2.87 (1.43-3.87), respectively].
Conclusions: 3D reconstruction models play a significant role in modifying surgeons' strategy and surgical planning for patients with renal tumors, especially for patients with stronger indications for a minimally invasive and/or nephron-sparing approach.
Keywords: Neoplasms; Nephrectomy; Surgical Procedures, Operative.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expanding the Indications of Robotic Partial Nephrectomy for Highly Complex Renal Tumors: Urologists' Perception of the Impact of Hyperaccuracy Three-Dimensional Reconstruction.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019 Feb;29(2):233-239. doi: 10.1089/lap.2018.0486. Epub 2018 Nov 3. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019. PMID: 30394820
-
Application of IRIS Three-Dimensional Anatomical Models As Preoperative Surgical Planning Tools in the Management of Localized Renal Masses.J Endourol. 2021 Mar;35(3):383-389. doi: 10.1089/end.2020.0405. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Endourol. 2021. PMID: 33451273
-
3D mixed reality holograms for preoperative surgical planning of nephron-sparing surgery: evaluation of surgeons' perception.Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2021 Jun;73(3):367-375. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.19.03610-5. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 31486325
-
Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.J Endourol. 2005 Jul-Aug;19(6):634-42. doi: 10.1089/end.2005.19.634. J Endourol. 2005. PMID: 16053351 Review.
-
Partial nephrectomy for renal tumors: recommendations of the Italian Society of Urology RCC working group.Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2024 Feb;76(1):9-21. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.24.05772-0. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38426419 Review.
Cited by
-
Three-Dimensional Virtual Model for Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN): Development of Study Protocol for Evaluation of the Learning Curve to Optimize the Precision and Accuracy of the 3D Imaging.Res Rep Urol. 2025 Feb 6;17:27-30. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S503524. eCollection 2025. Res Rep Urol. 2025. PMID: 39931350 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual reality-augmented differentiable simulations for digital twin applications in surgical planning.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 8;15(1):24377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99608-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40629031 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-TRUS fusion targeted biopsy is highligheted in International Brazilian Journal of Urology.Int Braz J Urol. 2023 May-Jun;49(3):278-280. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2023.03.01. Int Braz J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37115174 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Risk-adjusted trifecta outcomes in ultrasound-guided RFA of T1a renal masses: experi-ence from a large tertiary cancer center.Int Braz J Urol. 2025 Jul-Aug;51(4):e20250034. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2025.0034. Int Braz J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40327518 Free PMC article.
-
Extrarenal Visceral Arteries Injuries during Left Radical Nephrectomy: A 50-Year Continuing Problem.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 14;13(20):6125. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206125. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458075 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zargar H, Allaf ME, Bhayani S, Stifelman M, Rogers C, Ball MW, Larson J, Marshall S, Kumar R, Kaouk JH. Trifecta and optimal perioperative outcomes of robotic and laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in surgical treatment of small renal masses: a multi-institutional study. BJU Int. 2015;116:407–414. - PubMed
-
- Wang D, Zhang B, Yuan X, Zhang X, Liu C. Preoperative planning and real-time assisted navigation by three-dimensional individual digital model in partial nephrectomy with three-dimensional laparoscopic system. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2015;10:1461–1468. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Qi L, Yuan P, Zu X, Chen W, Cao Z, Li Y, et al. Application of Three-Dimensional Visualization Technology in Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy of Renal Tumor: A Comparative Study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2017;27:516–523. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Ge HW, Li NC, Yu CF, Guo HF, Jin SH, et al. Evaluation of three-dimensional printing for laparoscopic partial nephrectomy of renal tumors: a preliminary report. World J Urol. 2016;34:533–537. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
