Expression of Concern: Prognostic Role of Mucin Antigen MUC4 for Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37115797
- PMCID: PMC10146455
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285348
Expression of Concern: Prognostic Role of Mucin Antigen MUC4 for Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
Figures
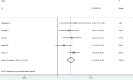

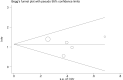
Expression of concern for
-
Prognostic Role of Mucin Antigen MUC4 for Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 15;11(6):e0157878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157878. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27305093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeh CN, Pang ST, Wu RC, Chen TW, Jan YY, Chen MF. Prognostic value of MUC4 for mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after hepatectomy. Oncol Rep. 2009; 21: 49–56 - PubMed
-
- Yanyu H. Expression and signification of MUC3 and MUC4 in hepatolithiasis associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. scholarly journal. M.Sc. Thesis, The University of south China, 2012
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

