Immune mechanisms of toxicity from checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 37117135
- PMCID: PMC10330206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.04.002
Immune mechanisms of toxicity from checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
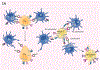
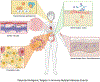
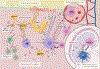
Immunotherapy has changed the treatment landscape for cancer over the past decade. Inhibitors of the immune checkpoint proteins cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen (CTLA)-4, programmed death (PD)-1, and PD ligand 1 (PD-L1) can induce durable remissions in a subset of patients with metastatic disease. However, these treatments can be limited by inflammatory toxicities that can affect any organ system in the body and in some cases can be life threatening. Considerable progress has been made in understanding the drivers of these toxicities as well as effective management strategies. Further research into understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms that drive toxicity will enable better prediction of toxicity and development of optimized therapies for these toxicities that avoid interfering with antitumor immunity. In this review, we discuss our current understanding of the inflammatory toxicities from immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and propose optimal treatment strategies for these toxicities.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; checkpoint blockade; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune-related adverse events; inflammatory toxicity.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.K.D. received research funding from Novartis, BMS, Eli Lilly, and Genocea and is a founder and advisory board member for Kojin Therapeutics. M.D. has received research funding from Eli Lilly; he has received consulting fees from Genentech, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Partner Therapeutics, SQZ Biotech, AzurRx, Eli Lilly, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Aditum, Foghorn Therapeutics, Palleon, Sorriso Pharmaceuticals, Generate Biomedicines, and Moderna; and he is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board for Neoleukin Therapeutics, Veravas, and Cerberus Therapeutics.
Figures

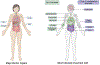
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

