Metals to combat antimicrobial resistance
- PMID: 37117903
- PMCID: PMC9907218
- DOI: 10.1038/s41570-023-00463-4
Metals to combat antimicrobial resistance
Abstract
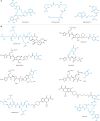
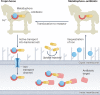
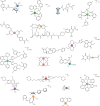
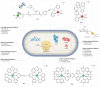
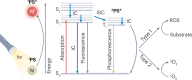
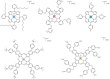
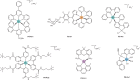
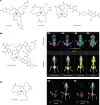
Bacteria, similar to most organisms, have a love-hate relationship with metals: a specific metal may be essential for survival yet toxic in certain forms and concentrations. Metal ions have a long history of antimicrobial activity and have received increasing attention in recent years owing to the rise of antimicrobial resistance. The search for antibacterial agents now encompasses metal ions, nanoparticles and metal complexes with antimicrobial activity ('metalloantibiotics'). Although yet to be advanced to the clinic, metalloantibiotics are a vast and underexplored group of compounds that could lead to a much-needed new class of antibiotics. This Review summarizes recent developments in this growing field, focusing on advances in the development of metalloantibiotics, in particular, those for which the mechanism of action has been investigated. We also provide an overview of alternative uses of metal complexes to combat bacterial infections, including antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and radionuclide diagnosis of bacterial infections.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- O’Neill, J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. (Government of the United Kingdom, 2016). Landmark report that analysed the impact of antimicrobial resistance from an economic perspective, which is the source of the highly quoted figure that antimicrobial resistance will cause 10 million deaths per year by 2050.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

