Systemic GDF11 attenuates depression-like phenotype in aged mice via stimulation of neuronal autophagy
- PMID: 37118117
- PMCID: PMC10154197
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-022-00352-3
Systemic GDF11 attenuates depression-like phenotype in aged mice via stimulation of neuronal autophagy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Systemic GDF11 attenuates depression-like phenotype in aged mice via stimulation of neuronal autophagy.Nat Aging. 2023 Aug;3(8):1036. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00454-6. Nat Aging. 2023. PMID: 37328576 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
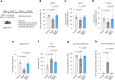
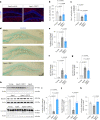
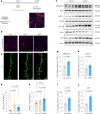
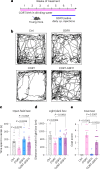
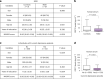
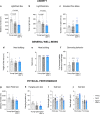
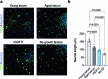
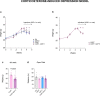
Cognitive decline and mood disorders increase in frequency with age. Many efforts are focused on the identification of molecules and pathways to treat these conditions. Here, we demonstrate that systemic administration of growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) in aged mice improves memory and alleviates senescence and depression-like symptoms in a neurogenesis-independent manner. Mechanistically, GDF11 acts directly on hippocampal neurons to enhance neuronal activity via stimulation of autophagy. Transcriptomic and biochemical analyses of these neurons reveal that GDF11 reduces the activity of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a master regulator of autophagy. Using a murine model of corticosterone-induced depression-like phenotype, we also show that GDF11 attenuates the depressive-like behavior of young mice. Analysis of sera from young adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) reveals reduced GDF11 levels. These findings identify mechanistic pathways related to GDF11 action in the brain and uncover an unknown role for GDF11 as an antidepressant candidate and biomarker.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
GDF11 reverses mood and memory declines in aging.Nat Aging. 2023 Feb;3(2):148-150. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00362-9. Nat Aging. 2023. PMID: 37118123 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

