Computational modeling and prediction of deletion mutants
- PMID: 37119820
- PMCID: PMC10247520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2023.04.005
Computational modeling and prediction of deletion mutants
Abstract
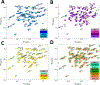
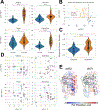
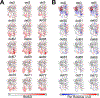
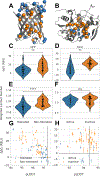
In-frame deletion mutations can result in disease. The impact of these mutations on protein structure and subsequent functional changes remain understudied, partially due to the lack of comprehensive datasets including a structural readout. In addition, the recent breakthrough in structure prediction through deep learning demands an update of computational deletion mutation prediction. In this study, we deleted individually every residue of a small α-helical sterile alpha motif domain and investigated the structural and thermodynamic changes using 2D NMR spectroscopy and differential scanning fluorimetry. Then, we tested computational protocols to model and classify observed deletion mutants. We show a method using AlphaFold2 followed by RosettaRelax performs the best overall. In addition, a metric containing pLDDT values and Rosetta ΔΔG is most reliable in classifying tolerated deletion mutations. We further test this method on other datasets and show they hold for proteins known to harbor disease-causing deletion mutations.
Keywords: AlphaFold; Deletion; Modeling; NMR; Rosetta; SAM domain; indel; mutation; ΔΔG.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.T.S. has received an unrelated research fund from Navigo Proteins GmbH, Halle (Saale), Germany. J.I.A. is currently affiliated with Molecular Pharmacology and Therapeutics Graduate Program, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA. All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Mind the gap.Structure. 2023 Jun 1;31(6):641-643. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2023.05.005. Structure. 2023. PMID: 37267922
References
-
- Rufenacht UB, Gouya L, Schneider-Yin X, Puy H, Schafer BW, Aquaron R, Nordmann Y, Minder EI, and Deybach JC (1998). Systematic analysis of molecular defects in the ferrochelatase gene from patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria. Am J Hum Genet 62, 1341–1352. 10.1086/301870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

