Review on two-dimensional material-based field-effect transistor biosensors: accomplishments, mechanisms, and perspectives
- PMID: 37122015
- PMCID: PMC10148958
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-01898-z
Review on two-dimensional material-based field-effect transistor biosensors: accomplishments, mechanisms, and perspectives
Abstract
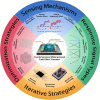
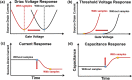
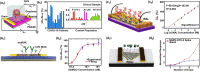
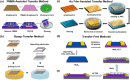
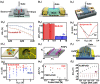
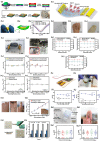
Field-effect transistor (FET) is regarded as the most promising candidate for the next-generation biosensor, benefiting from the advantages of label-free, easy operation, low cost, easy integration, and direct detection of biomarkers in liquid environments. With the burgeoning advances in nanotechnology and biotechnology, researchers are trying to improve the sensitivity of FET biosensors and broaden their application scenarios from multiple strategies. In order to enable researchers to understand and apply FET biosensors deeply, focusing on the multidisciplinary technical details, the iteration and evolution of FET biosensors are reviewed from exploring the sensing mechanism in detecting biomolecules (research direction 1), the response signal type (research direction 2), the sensing performance optimization (research direction 3), and the integration strategy (research direction 4). Aiming at each research direction, forward perspectives and dialectical evaluations are summarized to enlighten rewarding investigations.
Keywords: Biomarker detection; Biosensor; Field-effect transistor; Sensing application; Two-Dimensional Material.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Balderston S, Taulbee JJ, Celaya E, Fung K, Jiao A, Smith K, Hajian R, Gasiunas G, Kutanovas S, Kim D. Discrimination of single-point mutations in unamplified genomic DNA via Cas9 immobilized on a graphene field-effect transistor. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5:713–725. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00706-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

