The effect of voxelization in Monte Carlo simulation to validate Bragg peak characteristics for a pencil proton beam
- PMID: 37122904
- PMCID: PMC10132192
- DOI: 10.5603/RPOR.a2023.0007
The effect of voxelization in Monte Carlo simulation to validate Bragg peak characteristics for a pencil proton beam
Abstract
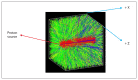
Background: The purpose of this research was to show how the Bragg peak (BP) characteristics were affected by changing the voxel size in longitudinal and transverse directions in Monte Carlo (MC) simulations by using Geant4 and to calculate BP characteristics accurately by considering the voxel size effect for 68 MeV and 235.81 MeV.
Materials and methods: Different interpolation techniques were applied to simulation data to find the closest results to the experimental data.
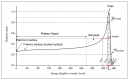
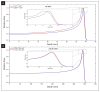
Results: When the x-size of the voxel was increased 2 times at low energy, the maximum dose increase in the entrance and plateau regions were 17.8% and 17%, respectively, while BP curve shifted to the shallower region, resulting in a 0.5 mm reduction in the curable tumor width (W80pd). At high energy, the maximum dose increase at the entrance and plateau regions were 0.4% and 0.6%, respectively, while it was observed that W80pd did not change. When the y-z sizes of the voxel were increased 2 times at low energy, the maximum dose reduction at the entrance and plateau regions was 3.4%, but no change was observed in W80pd. At high energy, when the y-z sizes of the voxel were increased 2.2 times, the maximum dose reduction at the entrance and plateau regions were 8.9% and 9.1%, respectively, while W80pd increased by 0.5 mm. When linear, cubic spline, and Akima interpolations were applied to the simulation data, it was found that the results closest to the experimental data were obtained for Akima interpolations for both energies.
Conclusion: it has been shown that the voxel size effect for the longitudinal direction was more effective at low energy than at high energy. However, the voxel size effect for the transverse direction was more effective for high energy.
Keywords: Bragg peak; Geant4; Monte Carlo simulations; proton therapy; voxel size effect.
© 2023 Greater Poland Cancer Centre.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Experimental depth dose curves of a 67.5 MeV proton beam for benchmarking and validation of Monte Carlo simulation.Med Phys. 2015 Jul;42(7):4199-210. doi: 10.1118/1.4922501. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26133619 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of GATE-RTion (GATE/Geant4) Monte Carlo simulation settings for proton pencil beam scanning quality assurance.Med Phys. 2020 Nov;47(11):5817-5828. doi: 10.1002/mp.14481. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32967037
-
Benchmarking a GATE/Geant4 Monte Carlo model for proton beams in magnetic fields.Med Phys. 2020 Jan;47(1):223-233. doi: 10.1002/mp.13883. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 31661559 Free PMC article.
-
An initial systematic study of the linear energy transfer distributions of a proton beam under a transverse magnetic field.Med Phys. 2022 Mar;49(3):1839-1852. doi: 10.1002/mp.15478. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 35124798
-
Monte Carlo simulations of ³He ion physical characteristics in a water phantom and evaluation of radiobiological effectiveness.Med Phys. 2016 Feb;43(2):761-76. doi: 10.1118/1.4939440. Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 26843239
Cited by
-
Heterogeneity in biological response of MDA-MB-231 cells after proton irradiation along different parts of the depth-dose curve: before, within, and behind the Bragg peak.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024 Oct 3;29(4):478-487. doi: 10.5603/rpor.102129. eCollection 2024. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024. PMID: 39895957 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis and Review of Radiation Dose Escalation in Definitive Radiation Therapy between Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma of Esophageal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 3;16(3):658. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030658. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
