Lipid metabolism of hepatocellular carcinoma impacts targeted therapy and immunotherapy
- PMID: 37123054
- PMCID: PMC10134209
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i4.617
Lipid metabolism of hepatocellular carcinoma impacts targeted therapy and immunotherapy
Abstract
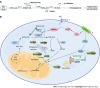
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignant tumor that affecting many people's lives globally. The common risk factors for HCC include being overweight and obese. The liver is the center of lipid metabolism, synthesizing most cholesterol and fatty acids. Abnormal lipid metabolism is a significant feature of metabolic reprogramming in HCC and affects the prognosis of HCC patients by regulating inflammatory responses and changing the immune microenvironment. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are being explored as the primary treatment strategies for HCC patients with unresectable tumors. Here, we detail the specific changes of lipid metabolism in HCC and its impact on both these therapies for HCC. HCC treatment strategies aimed at targeting lipid metabolism and how to integrate them with targeted therapy or immunotherapy rationally are also presented.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Lipid metabolism; Targeted therapy; Therapeutic efficacy.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Statin therapy: a potential adjuvant to immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 1;15:1324140. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1324140. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38362156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the amino acid metabolism-related gene signature for prognosis, tumor immune microenvironment, and candidate drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 13;13:1066773. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1066773. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36582227 Free PMC article.
-
[Strategies and challenges of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2020 Jun 20;28(6):457-460. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200602-00288. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32660170 Chinese.
-
A six lipid metabolism related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 1;12(1):20781. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25356-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36456877 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic dysregulation and emerging therapeutical targets for hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Feb;12(2):558-580. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.019. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35256934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chitosan-enclosed SLN improved SV-induced hepatocellular cell carcinoma death by modulation of IQGAP gene expression, JNK, and HDAC activities.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jul 18;51(1):824. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09757-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39023688
-
Statin therapy: a potential adjuvant to immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 1;15:1324140. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1324140. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38362156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene targets with therapeutic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):4543-4547. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i12.4543. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39678796 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan capped-NLCs enhanced codelivery of gefitinib and simvastatin into MDR HCC: impact of compositions on cell death, JNK3, and Telomerase.Oncol Res. 2025 Jan 16;33(2):477-492. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.053337. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 39866231 Free PMC article.
-
ERLNs augment simultaneous delivery of GFSV into PC-3 cells: Influence of drug combination on SDH, GPX-4, 5α-RD, and cytotoxicity.Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):919-935. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.054537. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40191728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2022;400:1345–1362. - PubMed
-
- Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V, Salem R, Sangro B, Singal AG, Vogel A, Fuster J, Ayuso C, Bruix J. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022;76:681–693. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

