Effects of plyometric training on kicking performance in soccer players: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37123265
- PMCID: PMC10133697
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1072798
Effects of plyometric training on kicking performance in soccer players: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
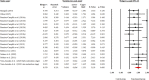
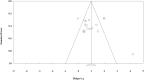
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the pooled effect size (ES) of plyometric training (PT) on kicking performance (kicking speed and distance) in soccer players depending upon some related factors (i.e., age, gender, skill level, and intervention duration). This study was carried out according to the PRISMA guidelines. Four electronic databases-EBSCO, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science-were searched for relevant studies. A total of n = 16 studies yielding 17 ES with n = 553 participants were finally included in the meta-analysis. A random-effects model was used to calculate Hedge's g with a 95% confidence interval (CI), which showed that plyometric training had a large-sized positive effect on soccer kicking performance (g = 0.979, 95% CI [0.606, 1.353], p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses were performed according to participants' characteristics (i.e., age, gender, skill level) and intervention duration, demonstrating no significant differences between these subgroups. The study pointed out that plyometric training is a generally effective method to improve soccer players' kicking performance, which plays a crucial role in passing and shooting actions during games. As for soccer players and strength and conditioning coaches, the plyometric training aiming to enhance kicking performance has valuable implications in practice. Therefore, besides well-known training methods like power training in the weight room, plyometric training could be incorporated into the overall strength and conditioning programs for soccer players to reach high standards of kicking performance.
Keywords: kicking distance; kicking speed; meta-analysis; plyometric training; soccer kicking.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Li, Gómez-Ruano, Memmert, Li and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of plyometric training on power and kicking distance in female adolescent soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jan;25(1):129-34. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b94a3d. J Strength Cond Res. 2011. PMID: 19966586
-
Effects of lower-limb plyometric training on body composition, explosive strength, and kicking speed in female soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Sep;23(6):1714-22. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b3f537. J Strength Cond Res. 2009. PMID: 19675492 Clinical Trial.
-
The Increased Effectiveness of Loaded Versus Unloaded Plyometric Jump Training in Improving Muscle Power, Speed, Change of Direction, and Kicking-Distance Performance in Prepubertal Male Soccer Players.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2020 Feb 1;15(2):189–195. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2018-0866. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2020. PMID: 31094246 Clinical Trial.
-
Plyometric Jump Training Effects on Maximal Strength in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized-Controlled Studies.Sports Med Open. 2024 May 10;10(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40798-024-00720-w. Sports Med Open. 2024. PMID: 38727944 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of plyometric training on technical skill performance among athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 17;18(7):e0288340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288340. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37459333 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of 12 weeks of high-intensity interval rope skipping training on speed and power indexes in male soccer players.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 10;13:1579535. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1579535. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40708856 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic review of the factors that affect soccer players' short-passing ability-based on the Loughborough Soccer Passing Test.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 Apr 26;16(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00880-y. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38671510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert M. (1991). Eccentric muscle training in sports and orthopedics. New York: Churchill Livingstone. Inc.
-
- Anderst W., Eksten F., Koceja D. (1994). 176 effects of plyometric and explosive resistance training on lower body power. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 26 (5), S31. 10.1249/00005768-199405001-00177 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials