The Role of Computed Tomography in the Management of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
- PMID: 37123712
- PMCID: PMC10139731
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.36821
The Role of Computed Tomography in the Management of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
Abstract
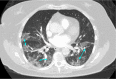
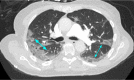
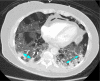
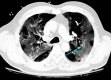
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 at the end of 2019 sparked the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Even though it was a novel virus, the workup of suspected COVID-19 included standard protocols used for the investigation of similar respiratory infections and pneumonia. One of the most important diagnostic tests in this regard is computed tomography (CT). CT scans have a high sensitivity in diagnosing COVID-19, and many of the characteristic imaging findings of COVID-19 are used in its diagnosis. The role of CT in COVID-19 management is expanding as more and more hospital practices adopt regular CT use in both the initial workup and continued care of COVID-19 patients. CT has helped hospitalists diagnose complications such as pulmonary embolism, subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, pneumothoraces, and nosocomial pneumonia. Although mainly used as a diagnostic tool, the prognostic role of CT in COVID-19 patients is developing. In this review, we explore the role of CT in the management of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, specifically elucidating its use as a diagnostic and prognostic modality, as well as its ability to guide hospital decision-making regarding complex cases. We will highlight important time points when CT scans are used: the initial encounter, the time at admission, and during hospitalization.
Keywords: computed tomography pulmonary angiography; covid-19; covid-19 pneumonia; ct (computed tomography) imaging; ground-glass opacity; hospitalized covid 19; outcomes in covid-19 hospitalizations; thromboembolism.
Copyright © 2023, Mir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
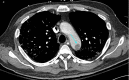
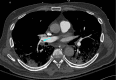

References
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215:87–93. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
