The toxicity associated with combining immune check point inhibitors with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 37124513
- PMCID: PMC10140561
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1158417
The toxicity associated with combining immune check point inhibitors with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
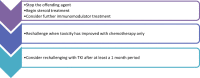
Latest advances in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) therapies have revolutionized the treatment regimens utilized for NSCLCs with or without a driver mutation. Molecular targeted treatments such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are utilized to prevent tumor progression and improve survival. Despite the great benefit of immunotherapy in NSCLC tumors with no driver mutation, the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in NSCLC tumors harboring a driver mutation has been under debate. Furthermore, several trials have been conducted investigating the use of these therapies with TKIs. A few trials were halted due to growing concerns of increased toxicity with the combination of TKI and immunotherapy. The adverse events ranged from low grade dermatologic complaints to fatal interstitial lung diseases. These toxicities occur with both concurrent and sequential administration of treatment. Thus, recommendations for the safest method of combination treatment have not yet been described. This review paper discusses recent views on combination treatment, previous clinical trials reporting grade 3-4 toxicities, and guidelines for a safe timeline of administration of treatment based on past evidence.
Keywords: combination; immunotherapy; lung cancer; pneumonitis; toxicity; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Kalra and Rashdan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous