Crude extracts of an endophytic fungus attenuate the growth of pathogenic bacteria in aquaculture
- PMID: 37124849
- PMCID: PMC10132345
- DOI: 10.18502/ijm.v14i3.9780
Crude extracts of an endophytic fungus attenuate the growth of pathogenic bacteria in aquaculture
Abstract
Background and objectives: Endophytic fungi are believed to possess compounds as antibacterial agents. This study was designed to determine in vivo antibacterial activity of the crude extracts from Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae IBRL OS-64 against pathogenic bacteria.
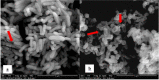
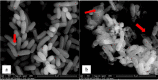
Materials and methods: The qualitative and quantitative screenings were performed using agar plug and disk diffusion antimicrobial tests, respectively. Besides that, the MIC and MBC value of the extracts were determined using broth microdilution assay and morphological changes of the bacterial cells exposed to the extract were observed under Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM).
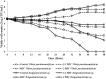
Results: Agar plug diffusion assay revealed that V. parahaemolyticus ATCC 17802 and Exiguobacterium profundum IBRL MA6 were the most sensitive to the extract with the size of inhibition zones of 11 to ≤ 20 mm. The MIC and MBC values of the extract varied depending on the test bacteria. Observation through SEM revealed that the bacterial cells exposed to the extract experienced severe damage such as irregular shape with crumpled and shrunken cells which led to cell death.
Conclusion: The data suggest that the crude extracts of L. pseudotheobromae IBRL OS-64 exert antibacterial activity against test bacteria and principally affect the cell wall in growing pathogenic bacterial cells.
Keywords: Antibacterial agents; Crude extracts; Disk diffusion antimicrobial tests.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures

References
-
- Marudhupandi T, Kumar TTA, Prakash S, Balamurugan J, Dhayanithi NB. Vibrio parahaemolyticus a causative bacterium for tail rot disease in ornamental fish, Amphiprion sebae. Aquac Rep 2017; 8: 39–44.
-
- Plant KP, Lapatra SE. Advances in fish vaccine delivery. Dev Comp Immunol 2011; 35: 1256–1262. - PubMed
-
- Soto-Rodriguez SA, Gomez-Gil B, Lozano-Olvera R, Betancourt-Lozano M, Morales-Covarrubias MS. Field and experimental evidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease of cultured shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in Northwestern Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 2015; 81: 1689–1699. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
