Nano drug-delivery systems for management of AIDS: liposomes, dendrimers, gold and silver nanoparticles
- PMID: 37125616
- PMCID: PMC10242436
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm-2022-0248
Nano drug-delivery systems for management of AIDS: liposomes, dendrimers, gold and silver nanoparticles
Abstract
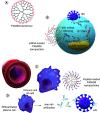
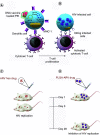
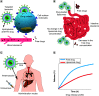
AIDS causes increasing mortality every year. With advancements in nanomedicine, different nanomaterials (NMs) have been applied to treat AIDS and overcome its limitations. Among different NMs, nanoparticles (NPs) can act as nanocarriers due to their enhanced solubility, sustained release, targeting abilities and facilitation of drug-dose reductions. This review discusses recent advancements in therapeutics for AIDS/HIV using various NMs, mainly focused on three classifications: polymeric, liposomal and inorganic NMs. Polymeric dendrimers, polyethylenimine-NPs, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-NPs, chitosan and the use of liposomal-based delivery systems and inorganic NPs, including gold and silver NPs, are explored. Recent advances, current challenges and future perspectives on the use of these NMs for better management of HIV/AIDS are also discussed.
Keywords: antiretroviral therapy; liposomes; nano drug-delivery system; nanomedicine; polymeric and inorganic nanoparticles.
Plain language summary
AIDS is a disease affecting many worldwide. Since it is difficult to cure AIDS, new therapies have been developed. Tiny materials called nanoparticles with promising features are used to carry different drugs to relevant organs in the body. There are various nanoparticles with different textures and shapes used in AIDS therapy. Branched nanoparticles, nanoparticles with repetitive building blocks and metal-based nanoparticles are three commonly used nanoparticles in AIDS treatment that are studied in this review. These tiny materials can find the exact place in the body to deliver drugs. They can also reduce the side effects of anti-AIDS drugs and help patients use fewer drugs while getting the same or better results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nano-Medicine as a Newly Emerging Approach to Combat Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018;6(1):17-27. doi: 10.2174/2211738506666180209095710. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29424324 Review.
-
Detecting and destroying cancer cells in more than one way with noble metals and different confinement properties on the nanoscale.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Nov 20;45(11):1854-65. doi: 10.1021/ar2003122. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22546051 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic nanomedicine--part 2.Nanomedicine. 2010 Oct;6(5):612-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 20417314 Review.
-
Hybrid Nanoplatforms Comprising Organic Nanocompartments Encapsulating Inorganic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Bioimaging Applications.Molecules. 2023 Jul 27;28(15):5694. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155694. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
Cited by
-
Polymeric and lipidic nanoparticles in transforming anti-HIV combinational therapy: can they turn the tide?Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 23. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04169-w. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40266304 Review.
-
Nanovesicles as Potential Carriers for Delivery of Antiviral Drugs: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2025;22(6):746-760. doi: 10.2174/0115672018313783240603114509. Curr Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 38847166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming Medicine with Nanobiotechnology: Nanocarriers and Their Biomedical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 23;16(9):1114. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091114. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Horizons in Antiretroviral Drug Delivery Systems for HIV Management.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(21):4192-4224. doi: 10.2174/0109298673306606240802111136. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39129289 Review.
-
Integrating computational insights in gold nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery: enhancing efficacy and precision.Front Med Technol. 2025 Feb 24;7:1528826. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2025.1528826. eCollection 2025. Front Med Technol. 2025. PMID: 40066057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oti VB. Nanoparticles and its implications in HIV/AIDS therapy. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 17(4), 448–456 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Rodrigo MAM, Heger Z, Cernei N et al. HIV biosensors–the potential of the electrochemical way. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 9(7), 3449–3457 (2014).
-
- Behrouz R, Topel CH, Seifi A et al. Risk of intracerebral hemorrhage in HIV/AIDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurovirol. 22(5), 634–640 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
