Pyrrolysine-Inspired in Cellulo Synthesis of an Unnatural Amino Acid for Facile Macrocyclization of Proteins
- PMID: 37125745
- PMCID: PMC10176472
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c01291
Pyrrolysine-Inspired in Cellulo Synthesis of an Unnatural Amino Acid for Facile Macrocyclization of Proteins
Abstract
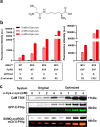
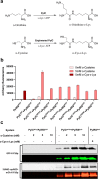
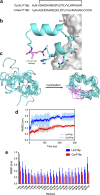
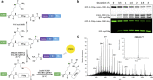
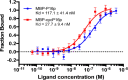
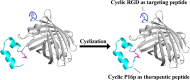
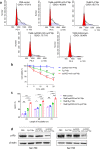
Macrocyclization has been touted as an effective strategy to enhance the in vivo stability and efficacy of protein therapeutics. Herein, we describe a scalable and robust system based on the endogenous biosynthesis of a noncanonical amino acid coupled to the pyrrolysine translational machinery for the generation of lasso-grafted proteins. The in cellulo biosynthesis of the noncanonical amino acid d-Cys-ε-Lys was achieved by hijacking the pyrrolysine biosynthesis pathway, and then, its genetical incorporation into proteins was performed using an optimized PylRS/tRNAPyl pair and cell line. This system was then applied to the structurally inspired cyclization of a 23-mer therapeutic P16 peptide engrafted on a fusion protein, resulting in near-complete cyclization of the target cyclic subunit in under 3 h. The resulting cyclic P16 peptide fusion protein possessed much higher CDK4 binding affinity than its linear counterpart. Furthermore, a bifunctional bicyclic protein harboring a cyclic cancer cell targeting RGD motif on the one end and the cyclic P16 peptide on the other is produced and shown to be a potent cell cycle arrestor with improved serum stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wilbs J.; Kong X.-D.; Middendorp S. J.; Prince R.; Cooke A.; Demarest C. T.; Abdelhafez M. M.; Roberts K.; Umei N.; Gonschorek P.; et al. Cyclic peptide FXII inhibitor provides safe anticoagulation in a thrombosis model and in artificial lungs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3890–3913. 10.1038/s41467-020-17648-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

