Protein intake and bone health: an umbrella review of systematic reviews for the evidence-based guideline of the German Nutrition Society
- PMID: 37126148
- PMCID: PMC10382330
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-023-06709-7
Protein intake and bone health: an umbrella review of systematic reviews for the evidence-based guideline of the German Nutrition Society
Abstract
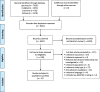
This umbrella review aimed at assessing whether a protein intake exceeding the current recommendation for younger (0.8 g/kg body weight [BW]/day) and older (1.0 g/kg BW/day) adults affects bone mineral density and fracture risk. Moreover, the effect of animal or plant protein was evaluated. A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews for systematic reviews (SRs) with or without meta-analysis of prospective studies published between 11/2008 and 08/2021. Methodological quality, outcome-specific certainty of evidence, and overall certainty of evidence of the retrieved SRs were assessed using established tools and predefined criteria. Eleven SRs of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and/or cohort studies were included. In SRs of cohort studies and RCTs, protein intake/kg BW/day ranged between 0.21-0.95 g (low intake) and > 1.24 g (high intake), respectively, and between 0.67-1.1 g (control groups) and 1.01-1.69 g (intervention groups), respectively. The vast majority of outcome-specific certainty of evidence was rated "low" or "very low." The overall certainty of evidence for an association (cohort studies) or effect (RCTs) of total, animal or plant protein intake on each of the investigated outcomes was rated "insufficient," with the exception of possible evidence for a reduced hip fracture risk by high vs. low protein intake. Since protein intakes in low/control and high/intervention groups were very heterogeneous and with low certainty of evidence, it remains unclear whether a dose above the current recommendation or type of protein intake (animal or plant protein) affects bone health overall. However, there is possible evidence for reduced hip fracture risk with high versus low protein intake.
Keywords: Bone health; Bone mineral density; Evidence-based guideline; Fracture risk; Protein; Umbrella review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A list of possible conflicts of interest is provided in Supplementary Material S10. Briefly, Heike Bischoff-Ferrari has received honorariums from WILD Pharma, DSM Nutritional Products, Fresenius, Roche, Meda, Sanofi, financial contributions from Schweizerischer Nationalfond, fundings from Pfizer, Vifor, Wild, Streuli Pharma, and medication from Omanda. Sarah Egert is member of the professional association of nutritionists (VDOE), German Nutrition Society (DGE), German Society for Nutritional Medicine (DGEM), and European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN). Sabine Ellinger has received various speaker honorariums and is member of the German Nutrition Society. Anja Kroke received financial contributions from technical health insurance (TK), owns shares from SATINA, has personal relationships to the company SATINA, and is member of the German Society for Epidemiology (DGEpi), medical chamber Hessen, and German Nutrition Society (DGE). Sandrine Louis owns shares from OP Food. Stefan Lorkowski is consultant for Akcea Therapeutics, AMGEN, Daiichi Sankyo, Danone, Sanofi-Aventis, Thüringer Ernährungsnetzwerk, has received honorarium for lecturing and training activities (Akcea Therapeutics, amedes, AMGEN, Berlin-Chemie, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Bund Niedergelassener Kardiologen, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD Sharp & Dohme, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Omnimed, Roche Pharma, Sanofi Aventis, Synlab, Unilever, Upfield), is member of the German Nutrition Society (DGE), German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), Federation of European Nutrition Societies (FENS), and participant in research projects for the development of reformulated food and participation in projects for improving food education. Matthias Schulze is member of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and German Society for Epidemiology (DGEpi). Lukas Schwingshackl is member of the GRADE Working Group. Roswitha Siener is member of the German Society for Urology (DGU) and German Academy of Nutritional Medicine (DAEM). Dorothee Volkert is member of the advisory board of the company Apetito, has received honorariums from Fresenius, Nestle, Nutricia, research funding from Nestec Ltd., and is member of the German Society for Nutritional Medicine (DGEM) German Nutrition Society, European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN). Bernhard Watzl is President of the German Nutrition Society (DGE). Gabriele Stangl, Armin Zittermann, Nicole Kalotai, Annemarie Schmidt, Julia Haardt, and Andreas Lehmann declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Chapter 68: Prevention of falls. In: Bilezikian JP, Bouillon R, Clemens T, et al., editors. Primer on the metabolic bone diseases and disorders of mineral metabolism. Wiley; 2018. pp. 526–533.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical