Identification and validation of immune-related biomarkers and potential regulators and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 37127580
- PMCID: PMC10150481
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01519-6
Identification and validation of immune-related biomarkers and potential regulators and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a major complication of diabetes and the leading cause of end-stage renal disease worldwide. Renal inflammation and infiltration of immune cells contribute to the development and progression of DKD. Thus, the aim of the present study was to identify and validate immune-related biomarkers and analyze potential regulators including transcription factors (TFs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and drugs for DKD.
Methods: Immune-related genes from the ImmPort database and glomeruli samples from GSE1009 and GSE30528 were used to identify differentially expressed immune-related genes (DEIRGs) of DKD. The expression level and clinical correlation analyses of DEIRGs were verified in the Nephroseq database. Murine podocytes were cultured to construct the high glucose-induced podocyte injury model. The reliability of the bioinformatics analysis was experimentally validated by RT-qPCR in podocytes. Networks among DEIRGs, regulators, and drugs were constructed to predict potential regulatory mechanisms for DKD.
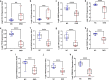
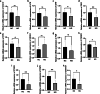
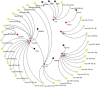
Results: DKD-associated DEIRGs were identified. CCL19 and IL7R were significantly upregulated in the DKD group and negatively correlated with glomerular filtration rate (GFR). GHR, FGF1, FYN, VEGFA, F2R, TGFBR3, PTGDS, FGF9, and SEMA5A were significantly decreased in the DKD group and positively correlated with GFR. RT-qPCR showed that the relative mRNA expression levels of GHR, FGF1, FYN, TGFBR3, PTGDS, FGF9, and SEMA5A were significantly down-regulated in the high glucose-induced podocyte injury group. The enriched regulators for DEIRGs included 110 miRNAs and 8 TFs. The abnormal expression of DEIRGs could be regulated by 16 established drugs.
Conclusions: This study identified immune-related biomarkers, regulators, and drugs of DKD. The findings of the present study provide novel insights into immune-related diagnosis and treatment of DKD.
Keywords: Diabetic kidney disease; Experimental validation; Immune-related biomarkers; Therapeutic drugs; Transcription factors; microRNAs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no competing interests in this manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Bioinformatic analysis of immune-related transcription factors in diabetic kidney disease].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Jun;40(6):488-493. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38952087 Chinese.
-
Identification of biomarkers related to iron death in diabetic kidney disease based on machine learning algorithms.Ann Hum Biol. 2025 Dec;52(1):2477248. doi: 10.1080/03014460.2025.2477248. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Ann Hum Biol. 2025. PMID: 40172091
-
Single-cell RNA and transcriptome sequencing profiles identify immune-associated key genes in the development of diabetic kidney disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 29;14:1030198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1030198. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37063851 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Role of microRNAs and mRNAs in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Review.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(6):e201023222412. doi: 10.2174/0115733998270983231009094216. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 37867275 Review.
-
Research progress on exosomes in podocyte injury associated with diabetic kidney disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 20;14:1129884. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1129884. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37020588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atherogenic Index of Plasma as an Early Marker of Chronic Kidney Disease and Liver Injury in Type 2 Diabetes.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2024 Jun 9;17:11795514241259741. doi: 10.1177/11795514241259741. eCollection 2024. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38859965 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol protects against diabetic nephropathy by modulating immune-related pathways: a bioinformatics and experimental validation.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Apr 15;17(4):2467-2483. doi: 10.62347/CBIP6642. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40385066 Free PMC article.
-
A genotype-guided prediction model for the incidence of persistent acute kidney injury following lung transplantation.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Dec 18;25(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03871-w. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39696008 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the mechanism of resveratrol in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation.J Transl Med. 2023 Jun 12;21(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04233-0. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37308949 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing the molecular landscape of diabetic nephropathy: Insights from machine learning and experiment verification.J Diabetes Investig. 2025 Aug;16(8):1473-1486. doi: 10.1111/jdi.70026. Epub 2025 Jun 5. J Diabetes Investig. 2025. PMID: 40470717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang T, Chi Y, Ren Y, Du C, Shi Y, Li Y. Resveratrol reduces oxidative stress and apoptosis in podocytes via Sir2-related enzymes, sirtuins1 (SIRT1)/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ co-activator 1α (PGC-1α) axis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:1220–1231. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911714. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

