Anti-proliferative potential and oxidative reactivity of thermo-oxidative degradation products of stigmasterol and stigmasteryl esters for human intestinal cells
- PMID: 37127788
- PMCID: PMC10151334
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34335-0
Anti-proliferative potential and oxidative reactivity of thermo-oxidative degradation products of stigmasterol and stigmasteryl esters for human intestinal cells
Abstract
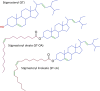
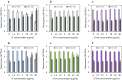
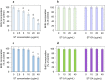
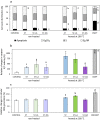
Stigmasterol in free and esterified form is incorporated in LDL cholesterol-lowering food products, intended for direct consumption and cooking, baking, and frying. Under thermal treatment, stigmasterol compounds may constitute a source of thermo-oxidative degradation products and oxyderivatives with potentially adverse health effects. This study aimed to analyze the anti-proliferative potential and genotoxicity of thermo-oxidatively treated stigmasterol (ST), stigmasteryl linoleate (ST-LA), and oleate (ST-OA). The effects on cell viability and proliferation, cell cycle progression, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and DNA damage were analyzed in normal human intestinal cells. The mutagenic potential was assessed in a bacterial reverse mutation test using Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains involving metabolic activation. Stigmasteryl esters showed a significantly lower potential to affect intestinal cell viability and proliferation than non-esterified ST, regardless of heating. Thermo-oxidatively treated ST suppressed intestinal cell proliferation by arresting the cell cycle in the G2/M phase and DNA synthesis inhibition. The enhanced intracellular ROS generation and caspase 3/7 activity suggest targeting intestinal cells to the apoptosis pathway. Also, heated ST-LA intensified ROS production and elicited pro-apoptotic effects. Thermo-oxidative derivatives of ST and ST-LA may evoke harmful gastrointestinal effects due to their high oxidative reactivity towards intestinal cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
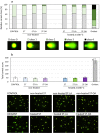
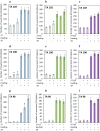
References
-
- EFSA Panel on Food additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS) Scientific opinion on the safety of stigmasterol-rich plant sterols as food additive. EFSA J. 2012;10:2659.
-
- Feng S, Wang L, Shao P, Sun P, Yang CS. A review on chemical and physical modifications of phytosterols and their influence on bioavailability and safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022;62:5638–5657. - PubMed
-
- Hovenkamp E, et al. Biological effects of oxidized phytosterols: A review of the current knowledge. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008;47:37–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

