Intractable Pleural Effusion After Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer
- PMID: 37128529
- PMCID: PMC10148733
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.36925
Intractable Pleural Effusion After Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer
Abstract
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) is an effective and attractive treatment option for patients who are poor surgical candidates. This case report describes a rare but serious complication of intractable pleural effusion after SABR for early-stage lung cancer. The patient was an 89-year-old woman with a medical history of early-stage breast cancer who was treated with partial resection and postoperative radiotherapy of 50 gray (Gy) in 25 fractions. SABR using 55 Gy in four fractions was conducted for lung lesions. The patient developed a pleural effusion that was refractory to conservative management and required multiple interventions, including repeated thoracentesis. This case report emphasizes the importance of monitoring and managing pleural effusion in patients with lung cancer receiving radiotherapy.
Keywords: adverse event; complication; early-stage lung cancer; pleural effusion; stereotactic ablative radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2023, Katano et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Radiation therapy planning support software, SYNAPSE Radiotherapy, was provided by FUJIFILM Corporation (Tokyo, Japan) under a research collaboration agreement.
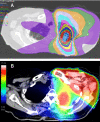
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard radiotherapy in stage 1 non-small-cell lung cancer (TROG 09.02 CHISEL): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Apr;20(4):494-503. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30896-9. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30770291 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Salvage Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Isolated Lung Recurrence of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase II Clinical Trial.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Jun;12(6):983-992. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.02.018. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28259750 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Is stereotactic ablative radiotherapy equivalent to sublobar resection in high-risk surgical patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013 Nov;17(5):845-53. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivt262. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23900381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pericardial Oligometastasis From Merkel Cell Carcinoma Treated With Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy.Cureus. 2025 Mar 1;17(3):e79903. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79903. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40171353 Free PMC article.
-
Is radiofrequency ablation more effective than stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in patients with early stage medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012 Aug;15(2):258-65. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivs179. Epub 2012 May 10. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012. PMID: 22581864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
