Anxiety and depression: A top-down, bottom-up model of circuit function
- PMID: 37129246
- PMCID: PMC10695657
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.14997
Anxiety and depression: A top-down, bottom-up model of circuit function
Abstract
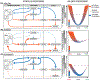
A functional interplay of bottom-up and top-down processing allows an individual to appropriately respond to the dynamic environment around them. These processing modalities can be represented as attractor states using a dynamical systems model of the brain. The transition probability to move from one attractor state to another is dependent on the stability, depth, neuromodulatory tone, and tonic changes in plasticity. However, how does the relationship between these states change in disease states, such as anxiety or depression? We describe bottom-up and top-down processing from Marr's computational-algorithmic-implementation perspective to understand depressive and anxious disease states. We illustrate examples of bottom-up processing as basolateral amygdala signaling and projections and top-down processing as medial prefrontal cortex internal signaling and projections. Understanding these internal processing dynamics can help us better model the multifaceted elements of anxiety and depression.
Keywords: PFC; amygdala; anxiety; attractor states; bottom-up; depression; top-down.
© 2023 The Authors. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

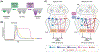
Similar articles
-
Emotion reactivity-related brain network analysis in generalized anxiety disorder: a task fMRI study.BMC Psychiatry. 2020 Sep 2;20(1):429. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02831-6. BMC Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32878626 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic causal modeling in PTSD and its dissociative subtype: Bottom-up versus top-down processing within fear and emotion regulation circuitry.Hum Brain Mapp. 2017 Nov;38(11):5551-5561. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23748. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017. PMID: 28836726 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion regulation and trait anxiety are predicted by the microstructure of fibers between amygdala and prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 15;35(15):6020-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3659-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25878275 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanistic model for individualised treatment of anxiety disorders based on predictive neural biomarkers.Psychol Med. 2020 Apr;50(5):727-736. doi: 10.1017/S0033291720000410. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Psychol Med. 2020. PMID: 32204741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Top-down and bottom-up factors in threat-related perception and attention in anxiety.Biol Psychol. 2016 Dec;121(Pt B):160-172. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Biol Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27546616 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell- and Pathway-Specific Disruptions in the Accumbens of Fragile X Mouse.J Neurosci. 2024 Jul 24;44(30):e1587232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1587-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38830765 Free PMC article.
-
Increased functional integration of emotional control network in late adulthood.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 9:2024.04.10.588823. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.10.588823. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38659752 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Heterosynaptic Regulation of α2A-Adrenoceptors on Glutamate/GABA Release in the Prefrontal Cortex of Rats.Biomedicines. 2025 May 28;13(6):1322. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061322. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564041 Free PMC article.
-
Basolateral amygdala volume in affective disorders using 7T MRI in vivo.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 6;15:1404594. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1404594. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39834577 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal serotonin signalling dynamically influences the development of cortical GABAergic circuits with consequences for lifelong sensory encoding.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 4;16(1):5203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59659-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40467568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kessler RC, Angermeyer M, Anthony JC, De Graaf R, Demyttenaere K, Gasquet I, De Girolamo G, Gluzman S, Gureje O, Haro JM, Kawakami N, Karam A, Levinson D, Medina Mora ME, Oakley Browne MA, Posada-Villa J, Stein DJ, Adley Tsang CH, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, … Ustün TB (2007). Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of mental disorders in the World Health Organization’s World Mental Health Survey Initiative. World Psychiatry, 6, 168–176. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marr D, & Poggio T (1976). From understanding computation to understanding neural circuitry.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

