Combined ARFI and Shear Wave Imaging of Prostate Cancer: Optimizing Beam Sequences and Parameter Reconstruction Approaches
- PMID: 37129257
- PMCID: PMC10660585
- DOI: 10.1177/01617346231171895
Combined ARFI and Shear Wave Imaging of Prostate Cancer: Optimizing Beam Sequences and Parameter Reconstruction Approaches
Abstract
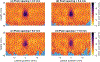
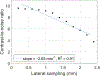
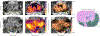
This study demonstrates the implementation of a shear wave reconstruction algorithm that enables concurrent acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging and shear wave elasticity imaging (SWEI) of prostate cancer and zonal anatomy. The combined ARFI/SWEI sequence uses closely spaced push beams across the lateral field of view and simultaneously tracks both on-axis (within the region of excitation) and off-axis (laterally offset from the excitation) after each push beam. Using a large number of push beams across the lateral field of view enables the collection of higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) shear wave data to reconstruct the SWEI volume than is typically acquired. The shear wave arrival times were determined with cross-correlation of shear wave velocity signals in two dimensions after 3-D directional filtering to remove reflection artifacts. To combine data from serially interrogated lateral push locations, arrival times from different pushes were aligned by estimating the shear wave propagation time between push locations. Shear wave data acquired in an elasticity lesion phantom and reconstructed using this algorithm demonstrate benefits to contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) with increased push beam density and 3-D directional filtering. Increasing the push beam spacing from 0.3 to 11.6 mm (typical for commercial SWEI systems) resulted in a 53% decrease in CNR. In human in vivo data, this imaging approach enabled high CNR (1.61-1.86) imaging of histologically-confirmed prostate cancer. The in vivo images had improved spatial resolution and CNR and fewer reflection artifacts as a result of the high push beam density, the high shear wave SNR, the use of multidimensional directional filtering, and the combination of shear wave data from different push beams.
Keywords: acoustic radiation force; prostate cancer; shear wave imaging; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Conflict of Interest: K. R. Nightingale and M. L. Palmeri have intellectual property related to radiation force-based imaging technologies that has been licensed to Siemens, Samsung, and MicroElastic Ultrasound Systems.
Figures
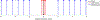





Similar articles
-
Multi-source and multi-directional shear wave generation with intersecting steered ultrasound push beams.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2015 Apr;62(4):647-62. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2014.006805. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2015. PMID: 25881343 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing stiffness of human prostates using acoustic radiation force.Ultrason Imaging. 2010 Oct;32(4):201-13. doi: 10.1177/016173461003200401. Ultrason Imaging. 2010. PMID: 21213566 Free PMC article.
-
Shear Wave Elasticity Imaging Using Nondiffractive Bessel Apodized Acoustic Radiation Force.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2021 Dec;68(12):3528-3539. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2021.3095614. Epub 2021 Nov 23. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2021. PMID: 34236961 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric Ultrasound Imaging of Prostate Cancer Using Deep Neural Networks.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024 Nov;50(11):1716-1723. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39174376
-
Prostate Cancer Detection Using 3-D Shear Wave Elasticity Imaging.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021 Jul;47(7):1670-1680. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33832823 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Amplitude-Modulation Frequency Optimization for Enhancing Harmonic Motion Imaging Performance of Breast Tumors in the Clinic.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025 Jan;51(1):169-179. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2024.09.021. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39428259
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

