The Impact of Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Monoclonal Antibodies with and without Apheresis on Platelet Aggregation in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 37129685
- PMCID: PMC11438737
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-023-07455-y
The Impact of Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Monoclonal Antibodies with and without Apheresis on Platelet Aggregation in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
Background and aims: It is well known that elevated cholesterol is associated with enhanced platelet aggregation and patients suffering from familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) have a high risk of thrombotic cardiovascular events. Although decreasing cholesterol level is associated with attenuation of platelet hyperactivity, there are currently no data on the effect of convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 monoclonal antibodies (PCSK9ab) on platelet reactivity in FH. The aim of the study was to analyse the impact of different therapies including PCSK9ab on platelet aggregation in FH.
Methods: This study enrolled all 15 patients treated in the University Hospital Hradec Králové for FH. PCSK9ab have been administered in 12 of 15 patients while 8 patients were also undergoing lipid apheresis. Blood samples from all patients including pre- and post-apheresis period were tested for platelet aggregation triggered by 7 inducers, and the effect of 3 clinically used drugs (acetylsalicylic acid, ticagrelor and vorapaxar) was compared as well.
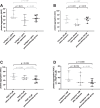
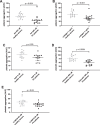
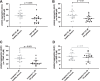
Results: Although apheresis decreased the reactivity of platelets in general, platelet responses were not different between non-apheresis patients treated with PCSK9ab and apheresis patients (post-apheresis values) with the exception of ristocetin. However, when compared to age-matched healthy population, FH patients had significantly lower platelet aggregation responses to 4 out of 7 used inducers and higher profit from 2 out of 3 used antiplatelet drugs even after exclusion of FH patients regularly receiving conventional antiplatelet treatment.
Conclusion: This study showed for the first time the suitability of PCSK9ab treatment for reduction of platelet reactivity in FH patients.
Keywords: ADP receptor; Acetylsalicylic acid; Antiplatelet; Dyslipidemia; Ticagrelor; Vorapaxar.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

