Withaferin A for COVID-19: a Network Pharmacology Approach
- PMID: 37129739
- PMCID: PMC10152032
- DOI: 10.1007/s12010-023-04525-7
Withaferin A for COVID-19: a Network Pharmacology Approach
Abstract
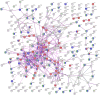
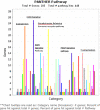
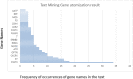
COVID-19 has become a global challenge as there are very few treatment options available. This has proved to impact several physiological implications like immunological injury, myocardial infarction, micro-thrombus formation, neurological complications and multi-organ dysfunction. A combination therapy or a systems pharmacology approach can be adopted to fight against COVID-19. Here, we have proposed withaferin A as a system pharmacophore employing molecular docking strategy using AutoDock Vina and utilising different bioinformatics tools like PharmMapper, STRING database and PANTHER Pathway enrichment analysis. Docking results show that withaferin A exhibits a significant binding affinity with P2Y12 receptor, vitamin D-binding protein and annexin A5, hence implying that it could play a role in anti-thrombosis. Protein-protein interaction network showed its importance in innate immune system. Results also show that this molecule may have significant potential to modulate T cell activation too. Text mining results showed association of STAT3 with withaferin A. Our studies propose that withaferin A might also conquer the cytokine storm via STAT3. This study concludes that two strong targets of withaferin A, i.e. vitamin D-binding protein and STAT3, have been identified and that withaferin A can be used as a system pharmacophore for drug development in order to combat COVID-associated complicacies.
Keywords: Antithrombotic; COVID-19; Immunomodulation; Neuro-inflammation; Withaferin A.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ravindran R, Sharma N, Roy S, Thakur AR, Ganesh S, Kumar S, Devi J, Rajkumar J. Interaction studies of Withania somnifera’s key metabolite withaferin A with different receptors assosciated with cardiovascular disease. Current Computer-Aided Drug Design. 2015;11:212–221. doi: 10.2174/1573409912666151106115848. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

