Potential biomarkers for diagnosis and disease evaluation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 37130223
- PMCID: PMC10309524
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002171
Potential biomarkers for diagnosis and disease evaluation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
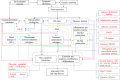
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic progressive lung disease characterized by progressive lung fibrogenesis and histological features of usual interstitial pneumonia. IPF has a poor prognosis and presents a spectrum of disease courses ranging from slow evolving disease to rapid deterioration; thus, a differential diagnosis remains challenging. Several biomarkers have been identified to achieve a differential diagnosis; however, comprehensive reviews are lacking. This review summarizes over 100 biomarkers which can be divided into six categories according to their functions: differentially expressed biomarkers in the IPF compared to healthy controls; biomarkers distinguishing IPF from other types of interstitial lung disease; biomarkers differentiating acute exacerbation of IPF from stable disease; biomarkers predicting disease progression; biomarkers related to disease severity; and biomarkers related to treatment. Specimen used for the diagnosis of IPF included serum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, lung tissue, and sputum. IPF-specific biomarkers are of great clinical value for the differential diagnosis of IPF. Currently, the physiological measurements used to evaluate the occurrence of acute exacerbation, disease progression, and disease severity have limitations. Combining physiological measurements with biomarkers may increase the accuracy and sensitivity of diagnosis and disease evaluation of IPF. Most biomarkers described in this review are not routinely used in clinical practice. Future large-scale multicenter studies are required to design and validate suitable biomarker panels that have diagnostic utility for IPF.
Copyright © 2023 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of surfactant protein A, surfactant protein D, Clara cell protein 16, S100 protein, trefoil factor 3, and prostatic secretory protein 94 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and chronic pulmonary obstructive disease.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2016 Oct 7;33(3):224-234. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2016. PMID: 27758987
-
S100A9 in BALF is a candidate biomarker of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Med. 2012 Apr;106(4):571-80. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2011.12.010. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Respir Med. 2012. PMID: 22209187
-
Gremlin-1 for the Differential Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Versus Other Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Clinical and Pathophysiological Analysis.Lung. 2021 Jun;199(3):289-298. doi: 10.1007/s00408-021-00440-y. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Lung. 2021. PMID: 33770226 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Application of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Analysis in Cases of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in which Diagnosis Cannot Be Confirmed by High-Resolution Computed Tomography.Lung. 2025 Jan 3;203(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s00408-024-00758-3. Lung. 2025. PMID: 39751999 Review.
-
Biomarkers and their potential functions in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020 Jun;14(6):593-602. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2020.1745066. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32187497 Review.
Cited by
-
Consecutive intrabronchial administration of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in ECMO-supported pediatric patients with end-stage interstitial lung disease: a safety and feasibility study (CIBA method).Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Apr 5;16(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04289-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40188166 Free PMC article.
-
Association between genetic prediction of 486 blood metabolites and the risk of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A mendelian randomization study.Biomed Rep. 2025 Jan 23;22(3):52. doi: 10.3892/br.2025.1930. eCollection 2025 Mar. Biomed Rep. 2025. PMID: 39931651 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary fibrosis through the prism of NLRP3 inflammasome: mechanistic pathways and prospective therapeutic innovations.Front Immunol. 2025 May 5;16:1593729. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593729. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40391214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis diagnosis and treatment.Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2025 Mar 7;3(1):12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2025.02.001. eCollection 2025 Mar. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40226606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causal relationship between serum metabolites and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Insights from a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 10;10(16):e36125. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36125. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39229516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solomon JJ, Chung JH, Cosgrove GP, Demoruelle MK, Fernandez-Perez ER, Fischer A, et al. . Predictors of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J 2016; 47:588–596. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00357-2015. - PubMed
-
- Morell F, Villar A, Montero MÁ, Muñoz X, Colby TV, Pipvath S, et al. . Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A prospective case-cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 2013; 1:685–694. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70191-7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

