Risk factors for the development of tuberculosis among the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37130994
- PMCID: PMC10354179
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-023-04988-0
Risk factors for the development of tuberculosis among the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Pediatric tuberculosis is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in children due to high transmission, poor diagnostic tools, and various respiratory diseases mimicking TB. Identifying risk factors will provide evidence for clinicians to strongly relate their diagnosis to the associated pathology. Studies were retrieved from PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar, systematically reviewed, and meta-analyzed for various risk factors and their association with pediatric TB. Meta-analysis depicted that four out of eleven risk factors were significant-contact with known TB cases (OR 6.42 [3.85,10.71]), exposure to smoke (OR 2.61 [1.24, 5.51]), overcrowding in the houses (OR 2.29 [1.04, 5.03]), and, poor household conditions (OR 2.65 [1.38, 5.09]). Although significant odds ratio estimates were obtained, we observed heterogeneity in the studies included. Conclusion: The study findings demand the constant screening of risk factors such as contact with known TB cases, exposure to smoke, overcrowding, and, poor household conditions for the development of pediatric TB. What is Known: • Knowledge of the risk factors of a disease is of utmost importance in the planning and institution of its control measures. Well-established risk factors in the occurrence of TB in the pediatric group are HIV positivity, older age and close contact with a known case of TB. What is New: • In addition to what is already known; this review and meta-analysis has identified exposure to indoor smoking, overcrowding and poor household conditions as important risk factors for developing pediatric TB. • Implications of the study: The findings highlight that in addition to routine contact screening for the pediatric group, the children living in poor household conditions and getting exposed to passive indoor smoking demand more attention to prevent the development of pediatric TB.
Keywords: High-burden countries; Pediatric; Risk factors; Tuberculosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
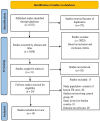


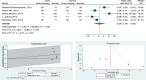
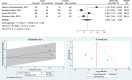
References
-
- WHO TB report- 2021 page- 04 accessed on 02th June, 2022. https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports
-
- WHO TB report- 2012 page- 14 accessed on 02th June, 2022. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/75938/9789241564502_eng...
-
- Attah C, Oguche S, Egah D, Ishaya T, Banwat M, Adgidzi A. Risk factors associated with paediatric tuberculosis in an endemic setting. Alexandria Journal of Medicine. 2018;54(4):403–409. doi: 10.1016/j.ajme.2018.05.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

