Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security and paths forward
- PMID: 37131070
- PMCID: PMC10153038
- DOI: 10.1038/s41579-023-00900-7
Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security and paths forward
Abstract
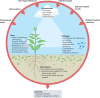
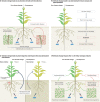
Plant disease outbreaks pose significant risks to global food security and environmental sustainability worldwide, and result in the loss of primary productivity and biodiversity that negatively impact the environmental and socio-economic conditions of affected regions. Climate change further increases outbreak risks by altering pathogen evolution and host-pathogen interactions and facilitating the emergence of new pathogenic strains. Pathogen range can shift, increasing the spread of plant diseases in new areas. In this Review, we examine how plant disease pressures are likely to change under future climate scenarios and how these changes will relate to plant productivity in natural and agricultural ecosystems. We explore current and future impacts of climate change on pathogen biogeography, disease incidence and severity, and their effects on natural ecosystems, agriculture and food production. We propose that amendment of the current conceptual framework and incorporation of eco-evolutionary theories into research could improve our mechanistic understanding and prediction of pathogen spread in future climates, to mitigate the future risk of disease outbreaks. We highlight the need for a science-policy interface that works closely with relevant intergovernmental organizations to provide effective monitoring and management of plant disease under future climate scenarios, to ensure long-term food and nutrient security and sustainability of natural ecosystems.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tripathi, A. N., Tiwari, S. K. & Behera, T. K. in Postharvest Technology Ch. 5 (ed. Ahiduzzaman, M. D.) (IntechOpen, 2022).
-
- Chakraborty S, Newton AC. Climate change, plant diseases and food security: an overview. Plant. Pathol. 2011;60:2–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02411.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

