Optimized enantioselective (S)-2-hydroxypropiophenone synthesis by free- and encapsulated-resting cells of Pseudomonas putida
- PMID: 37131175
- PMCID: PMC10155308
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-023-02073-7
Optimized enantioselective (S)-2-hydroxypropiophenone synthesis by free- and encapsulated-resting cells of Pseudomonas putida
Abstract
Background: Aromatic α-hydroxy ketones, such as S-2-hydroxypropiophenone (2-HPP), are highly valuable chiral building blocks useful for the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals and natural products. In the present study, enantioselective synthesis of 2-HPP was investigated by free and immobilized whole cells of Pseudomonas putida ATCC 12633 starting from readily-available aldehyde substrates. Whole resting cells of P. putida, previously grown in a culture medium containing ammonium mandelate, are a source of native benzoylformate decarboxylase (BFD) activity. BFD produced by induced P. putida resting cells is a highly active biocatalyst without any further treatment in comparison with partially purified enzyme preparations. These cells can convert benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde into the acyloin compound 2-HPP by BFD-catalyzed enantioselective cross-coupling reaction.
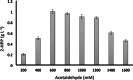
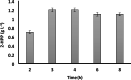
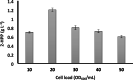
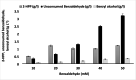
Results: The reaction was carried out in the presence of exogenous benzaldehyde (20 mM) and acetaldehyde (600 mM) as substrates in 6 mL of 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7) for 3 h. The optimal biomass concentration was assessed to be 0.006 g dry cell weight (DCW) mL- 1. 2-HPP titer, yield and productivity using the free cells were 1.2 g L- 1, 0.56 g 2-HPP/g benzaldehyde (0.4 mol 2-HPP/mol benzaldehyde), 0.067 g 2-HPP g- 1 DCW h- 1, respectively, under optimized biotransformation conditions (30 °C, 200 rpm). Calcium alginate (CA)-polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-boric acid (BA)-beads were used for cell entrapment. Encapsulated whole-cells were successfully employed in four consecutive cycles for 2-HPP production under aerobic conditions without any noticeable beads degradation. Moreover, there was no production of benzyl alcohol as an unwanted by-product.
Conclusions: Bioconversion by whole P. putida resting cells is an efficient strategy for the production of 2-HPP and other α-hydroxyketones.
Keywords: 2-Hydroxypropiophenone; Benzoylformate decarboxylase (BFD); Biotransformation; Cell immobilization; Pseudomonas putida; αHydroxyketones.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced chaotrope tolerance and (S)-2-hydroxypropiophenone production by recombinant Pseudomonas putida engineered with Pprl from Deinococcus radiodurans.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;17(3):e14448. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14448. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38498302 Free PMC article.
-
Acyloin formation by benzoylformate decarboxylase from Pseudomonas putida.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1699-704. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1699-1704.1992. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1622241 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the hydrostatic pressure and pH on the asymmetric 2-hydroxyketone formation catalyzed by Pseudomonas putida benzoylformate decarboxylase and variants thereof.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010 May 1;106(1):18-26. doi: 10.1002/bit.22650. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010. PMID: 20047192
-
Immobilization and characterization of benzoylformate decarboxylase from Pseudomonas putida on spherical silica carrier.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2011 Aug;34(6):671-80. doi: 10.1007/s00449-011-0516-0. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2011. PMID: 21286757
-
Bacterial mandelic acid degradation pathway and its application in biotechnology.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Aug;133(2):273-286. doi: 10.1111/jam.15529. Epub 2022 Apr 18. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35294082 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced chaotrope tolerance and (S)-2-hydroxypropiophenone production by recombinant Pseudomonas putida engineered with Pprl from Deinococcus radiodurans.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;17(3):e14448. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14448. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38498302 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Phosphate-Based Nanomaterials: Preparation, Multifunction, and Application for Bone Tissue Engineering.Molecules. 2023 Jun 15;28(12):4790. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124790. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kara S, Liese A. Enzymatic C-C bond formation, asymmetric. Encycl Ind Biotechnol. 2009:1–17.
-
- Sehl T, Bock S, Marx L, Maugeri Z, Walter L, Westphal R, et al. Asymmetric synthesis of (S)-phenylacetylcarbinol- closing a gap in C–C bond formation. Green Chem. 2017;19(2):380–4. doi: 10.1039/C6GC01803C. - DOI
-
- Wachtmeister J, Jakoblinnert A, Rother D. Stereoselective two-step biocatalysis in organic solvent: toward all stereoisomers of a 1, 2-diol at high product concentrations. Org Process Res Dev. 2016;20(10):1744–53. doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00232. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

