Target Trial Emulation to Improve Causal Inference from Observational Data: What, Why, and How?
- PMID: 37131279
- PMCID: PMC10400102
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000152
Target Trial Emulation to Improve Causal Inference from Observational Data: What, Why, and How?
Abstract
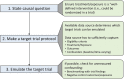
Target trial emulation has drastically improved the quality of observational studies investigating the effects of interventions. Its ability to prevent avoidable biases that have plagued many observational analyses has contributed to its recent popularity. This review explains what target trial emulation is, why it should be the standard approach for causal observational studies that investigate interventions, and how to do a target trial emulation analysis. We discuss the merits of target trial emulation compared with often used, but biased analyses, as well as potential caveats, and provide clinicians and researchers with the tools to better interpret results from observational studies investigating the effects of interventions.
Copyright © 2023 The Author. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

