This is a preprint.
Model-based hepatic percutaneous microwaveablation planning. First validation on a clinical dataset
- PMID: 37131766
- PMCID: PMC10153367
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2781339/v1
Model-based hepatic percutaneous microwaveablation planning. First validation on a clinical dataset
Update in
-
First validation of a model-based hepatic percutaneous microwave ablation planning on a clinical dataset.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 6;13(1):16862. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42543-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37803064 Free PMC article.
Abstract
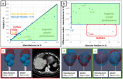
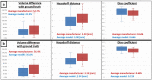
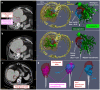
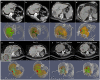
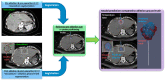
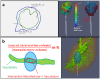
A model-based planning tool, integrated in an imaging system, is envisioned for CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation. This study aims to evaluate the biophysical model performance, by comparing its prediction retrospectively with the actualablation ground truth from a clinical data set in liver. The biophysical model uses a simplified formulation of heat depositionon the applicator and a heat sink related to vasculature to solve the bioheat equation. A performance metric is defined toassess how the planned ablation overlaps the actual ground truth. Results demonstrate superiority of this model predictioncompared to manufacturer tabulated data and a significant influence of the vasculature cooling effect. Nevertheless, vasculatureshortage due to branches occlusion and applicator misalignment due to registration error between scans affects the thermalprediction. With a more accurate vasculature segmentation, occlusion risk can be estimated, whereas branches can be usedas liver landmarks to improve the registration accuracy. Overall, this study emphasizes the benefit of a model-based thermalablation solution in better planning the ablation procedures. Contrast and registration protocols must be adapted to facilitate itsintegration into the clinical workflow.
Figures

References
-
- Kok H. et al. Heating technology for malignant tumors: a review. Int. J. Hyperth. 37, 711–741, DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2020.1779357 (2020). Funding Information: support for Robert Ivkov was provided by the National Cancer Institute [5R01CA194574–02 and 5R01CA247290] and the Jayne Koskinas Ted Giovanis Foundation for Health and Policy. Publisher Copyright: © 2020, © 2020 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

