OL-FS13 Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting miR-21-3p Expression
- PMID: 37132110
- PMCID: PMC10616927
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X21666230502111013
OL-FS13 Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting miR-21-3p Expression
Abstract
Background: OL-FS13, a neuroprotective peptide derived from Odorrana livida, can alleviate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (CI/R) injury, although the specific underlying mechanism remains to be further explored.
Objective: The effect of miR-21-3p on the neural-protective effects of OL-FS13 was examined.
Methods: In this study, the multiple genome sequencing analysis, double luciferase experiment, RT-qPCR, and Western blotting were used to explore the mechanism of OL-FS13.
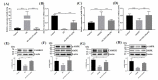
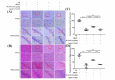
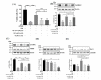
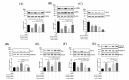
Results: Showed that over-expression of miR-21-3p against the protective effects of OL-FS13 on oxygen- glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/R)-damaged pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells and in CI/R-injured rats. miR-21-3p was then found to target calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2 (CAMKK2), and its overexpression inhibited the expression of CAMKK2 and phosphorylation of its downstream adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK), thereby inhibiting the therapeutic effects of OL-FS13 on OGD/R and CI/R. Inhibition of CAMKK2 also antagonized up-regulated of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2) by OL-FS13, thereby abolishing the antioxidant activity of the peptide.
Conclusion: Our results showed that OL-FS13 alleviated OGD/R and CI/R by inhibiting miR-21-3p to activate the CAMKK2/AMPK/Nrf-2 axis.
Keywords: CAMKK2/AMPK pathway; Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion; microRNA; neuroprotective; oxidative stress; peptide.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures




References
-
- Rapillo C.M., Donati M.C., Renieri L., Lombardo I., Addazio I., Betti M., Capasso F., Capirossi C., Giacomucci G., Lamassa M. Orbital infarction syndrome as a rare complication after mechanical thrombectomy in ischemic stroke. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2022 doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001659. [Epub Ahead of Print. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

