OPTN/SRTR 2021 Annual Data Report: Kidney
- PMID: 37132350
- PMCID: PMC9970360
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajt.2023.02.004
OPTN/SRTR 2021 Annual Data Report: Kidney
Abstract
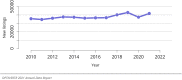
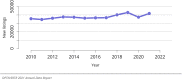
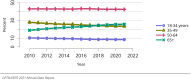
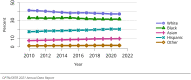
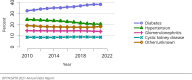
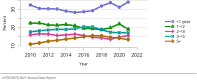
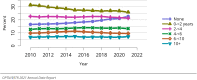
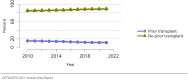
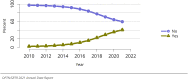
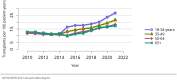
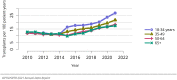
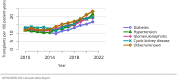
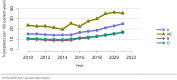
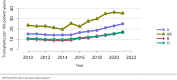
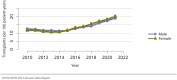
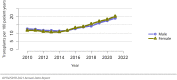
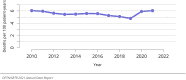
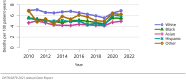
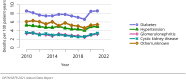
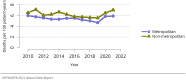
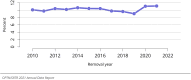
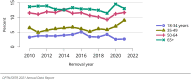
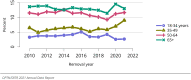
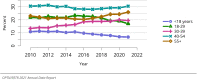
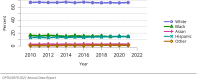
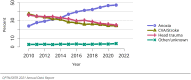
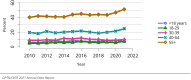
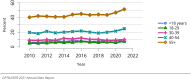
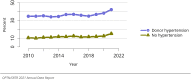
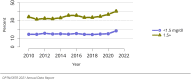
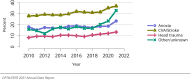
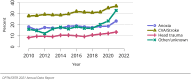
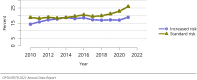
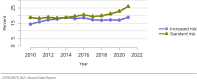
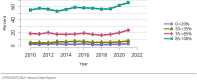
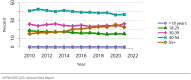
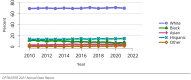
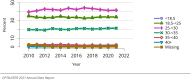
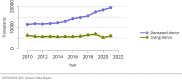
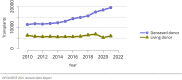
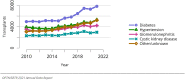
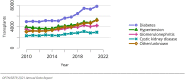
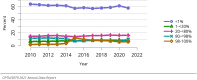
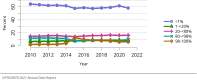
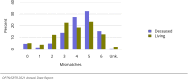
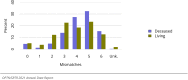
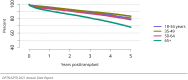
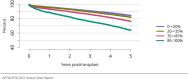
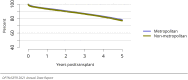
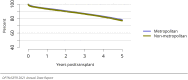
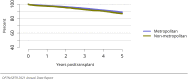
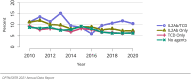
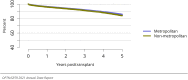
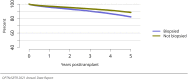
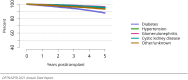
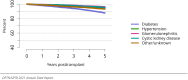
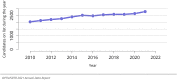
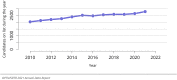
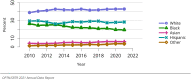
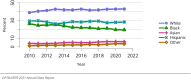
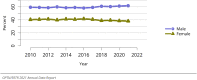
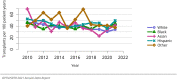
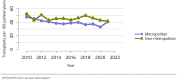
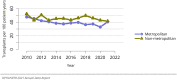
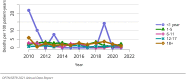
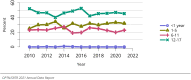
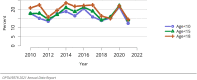
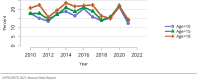
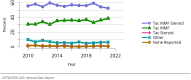
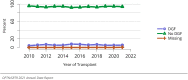
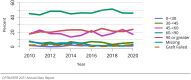
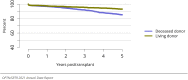
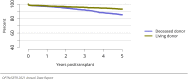
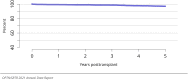
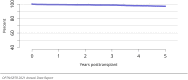
The year 2021 marked both successes and challenges for the field of kidney transplantation, in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and broader geographic organ distribution. The total number of kidney transplants in the United States reached a record count of 25,487, driven by growth in deceased donor kidney transplants. The total number of candidates listed for deceased donor kidney transplant rose slightly in 2021 but remained below 2019 listing levels, with nearly 10% of candidates having been waiting 5 years or longer. Pretransplant mortality declined slightly among candidates of Black, Hispanic, and other races, in parallel with increasing numbers of Black and Hispanic transplant recipients. In the context of broader organ sharing, there is growing disparity in pretransplant mortality among non-metropolitan compared with metropolitan residents. The proportion of deceased donor kidneys recovered but not used for transplant (nonuse rate) rose to a high of 24.6% overall, with greater nonuse among biopsied kidneys (35.9%), kidneys from donors aged 55 years or older (51.1%), and kidneys with kidney donor profile index (KDPI) of 85% or greater (66.6%). Nonuse of kidneys from donors who are hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody positive only slightly exceeded that of HCV antibody-negative donors. Disparities in access to living donor kidney transplant persists, especially for non-White and publicly insured patients. Delayed graft function continues an upward trend and occurred in 24% of adult kidney transplants in 2021. Five-year graft survival after living compared with deceased donor transplant was 88.6% versus 80.7% for recipients aged 18-34 years, and 82.1% versus 68.0% for recipients aged 65 years or older. The total number of pediatric kidney transplants performed increased to 820 in 2021, the highest number since 2010. Despite numerous efforts, living donor kidney transplant remains low among pediatric recipients, with continued racial disparities. The rate of deceased donor transplants among pediatric candidates recovered in 2021 from a low in 2020. Congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract remain the leading primary kidney disease diagnosis among pediatric candidates. Most pediatric deceased donor recipients receive a kidney from a donor with KDPI less than 35%. Graft survival continues to improve, with superior outcomes for living donor transplant recipients.
Keywords: Kidney transplant; transplant outcomes; waiting list outcomes.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

































































References
-
- Executive Office of the President Executive Order 13879 of July 10, 2019: Advancing American Kidney Health. 2019. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2019/07/15/2019-15159/ advanci...
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services Health Resources and Services Ad- ministration. New Rule Expands the Scope of Reimbursable Expenses for Living Or- gan Donation. 2020. https://www.hrsa.gov/about/ news/press-releases/new-rule-expands-scope-l...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

