Epidemiology and management of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in a Tunisian university hospital
- PMID: 37132406
- PMCID: PMC10512042
- DOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2018-070
Epidemiology and management of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in a Tunisian university hospital
Abstract
Introduction: Despite considerable advances in treatment, heart failure (HF) remains a serious public health problem linked to a high rate of mortality. The aim of this work was to describe the epidemiological, clinical and evolutionary features of HF in a Tunisian university hospital.
Methods: This was a retrospective study including 350 hospitalised patients diagnosed with HF with reduced ejection fraction (≤ 40%) during the period between 2013 and 2017.
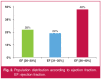
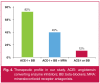
Results: The average age was 59 ± 12 years. A male predominance was noted. The main cardiovascular risk factor was the use of tobacco (47%). The electrocardiogram showed atrial fibrillation in 41% of patients and left bundle branch block in 36% of patients. Laboratory results revealed an electrolyte disorder in 30 cases, renal insufficiency in 25% of patients and anaemia in 20%. Echocardiography revealed reduced ejection fraction, with an average of 34 ± 6% (range: 20-40%). The main causes of HF were ischaemic heart disease in 157 patients. The most commonly used medications were diuretics (90% of patients), angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (88%), beta-blockers (91%) and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (35%). Cardiac resynchronisation therapy was performed on 30 patients and cardioverter defibrillator implantation on 15 patients. The hospital mortality rate was 10% and the average hospital stay was 12 ± 5 days. During six months of follow up, 56 patients died and 126 were re-admitted. Multivariate model predictors of six-month mortality were: age [odds ratio (OR): 8, p = 0.003], ischaemic HF (OR: 1.63, p = 0.01) and diabetes (OR: 21, p = 0.004).
Conclusion: This study illustrates the main characteristics of HF in our population. These include relatively young age, a predominance of males, ischaemic heart disease as the main aetiology, insufficient care strategies and a poor prognosis.
Keywords: Tunisia; aetiology; epidemiology; heart failure; treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Contemporary epidemiology and treatment of hospitalized heart failure patients in real clinical practice in China].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 24;47(11):865-874. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2019.11.004. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31744275 Chinese.
-
Impact of age on characteristics, performance measures and outcomes of inpatients for heart failure in Beijing, China.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Oct;10(5):2990-2997. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14487. Epub 2023 Aug 1. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37528635 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of patient survival rate after implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator without resynchronisation capability.Kardiol Pol. 2012;70(11):1099-110. Kardiol Pol. 2012. PMID: 23180517
-
Outcomes of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a Southeast Asian cohort.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2015 Sep;16(9):583-90. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000100. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2015. PMID: 25022929 Review.
-
Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Review.JAMA. 2020 Aug 4;324(5):488-504. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.10262. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32749493 Review.
Cited by
-
Unmet need for heart transplantation in Africa.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jun 24;86(8):4643-4646. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002311. eCollection 2024 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39118759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maggioni AD. Epidemiology of heart failure in Europe. Heart Fail Clin. 2015;11:625–635. - PubMed
-
- Geremy A, Jessup M. Understanding heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 2017;13:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, et al.. Focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults. Circulation. 2009;119(14):391–479. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

