Audiovisual Recording in the Inpatient Setting: A Method for Studying Parent-Nurse Communication
- PMID: 37133301
- PMCID: PMC10305750
- DOI: 10.1177/10748407231162131
Audiovisual Recording in the Inpatient Setting: A Method for Studying Parent-Nurse Communication
Abstract
Audiovisual recordings are under-utilized for capturing interactions in inpatient settings. Standardized procedures and methods improve observation and conclusion validity drawn from audiovisual data. This article provides specific approaches for collecting, standardizing, and maintaining audiovisual data based on a study of parent-nurse communication and child and family outcomes. Data were collected using audio and video recorders at defined time points simplifying its collection. Data were downloaded, edited for size and privacy, and securely stored, then transcribed, and subsequently reviewed to ensure accuracy. Positive working relationships with families and nurses facilitated successful study recruitment, data collection, and transcript cleaning. Barriers to recruitment and data collection, such as privacy concerns and technical issues, were successfully overcome. When carefully coordinated and obtained, audiovisual recordings are a rich source of research data. Thoughtful protocol design for the successful capture, storage, and use of recordings enables researchers to take quick action to preserve data integrity when unexpected situations arise.
Keywords: audiovisual recording; family nursing practice; parent-nurse communication; pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
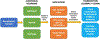
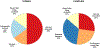
Figures
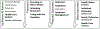
References
-
- Bonafide CP, Localio AR, Holmes JH, Nadkarni VM, Stemler S, MacMurchy M, Zander M, Roberts KE, Lin R, & Keren R (2017). Video analysis of factors associated with response time to physiologic monitor alarms in a children’s hospital. JAMA Pediatrics, 171(6), 524–531. 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.5123 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

