Disentangling between- and within-person alcohol and expectancy effects on acute alcohol craving
- PMID: 37133559
- PMCID: PMC10290517
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-023-06372-0
Disentangling between- and within-person alcohol and expectancy effects on acute alcohol craving
Abstract
Objective: Alcohol craving is a predictor of continued drinking and a diagnostic criterion for alcohol use disorder. Rewarding subjective effects potentiate craving, but it remains unclear if relations are expectancy-driven vs. alcohol-induced. In addition, it remains unclear if relations operate solely at the person level, or if there is also within-person dynamic change.
Methods: Participants (N = 448) come from a placebo-controlled alcohol administration study. Participants in the alcohol condition reported subjective effects and alcohol craving on ascending (BAC = .068), peak (BAC = .079), and descending (BAC = .066) BAC limbs. Participants in the placebo condition were yoked to alcohol condition participants. Multilevel models tested whether (1) within-person deviations in subjective effects predicted within-person deviations in craving, (2) between-person levels of subjective effects predicted between-person levels of craving, and (3) effects were dependent upon experimental condition.
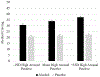
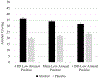
Results: At the within-person level, increases in high arousal positive/stimulant effects were associated with within-person increases in alcohol craving, regardless of experimental condition. At the between-person level, interactions were observed between high arousal positive/stimulant (and low arousal positive/relaxing) effects and condition. Probing suggested that the association between person-level high arousal positive/stimulant effects and craving was statistically significant in the alcohol but not the placebo condition. Conversely, the association between person-level low arousal positive/relaxing effects and craving was positive and statistically significant in the placebo but negative in the alcohol condition.
Conclusions: Findings suggest expectancy-like relations among high arousal positive/stimulant effects and craving within-person. However, alcohol-induced positive reinforcement (i.e., stimulation) facilitated heightened person-level craving, whereas expectancy-like negative reinforcement (i.e., relaxation) attenuated person-level craving.
Keywords: Alcohol craving; Alcohol expectancies; Placebo; Subjective response.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.).
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2022) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed. TR).
-
- Baker TB, Piper ME, McCarthy DE, Majeskie MR, Fiore MC (2004) Addiction motivation reformulated: an affective processing model of negative reinforcement. Psychol Rev 111(1):33–45 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

