Interrupting Endocrine Therapy to Attempt Pregnancy after Breast Cancer
- PMID: 37133584
- PMCID: PMC10358451
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2212856
Interrupting Endocrine Therapy to Attempt Pregnancy after Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Prospective data on the risk of recurrence among women with hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer who temporarily discontinue endocrine therapy to attempt pregnancy are lacking.
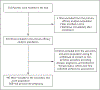
Methods: We conducted a single-group trial in which we evaluated the temporary interruption of adjuvant endocrine therapy to attempt pregnancy in young women with previous breast cancer. Eligible women were 42 years of age or younger; had had stage I, II, or III disease; had received adjuvant endocrine therapy for 18 to 30 months; and desired pregnancy. The primary end point was the number of breast cancer events (defined as local, regional, or distant recurrence of invasive breast cancer or new contralateral invasive breast cancer) during follow-up. The primary analysis was planned to be performed after 1600 patient-years of follow-up. The prespecified safety threshold was the occurrence of 46 breast cancer events during this period. Breast cancer outcomes in this treatment-interruption group were compared with those in an external control cohort consisting of women who would have met the entry criteria for the current trial.
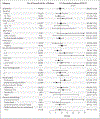
Results: Among 516 women, the median age was 37 years, the median time from breast cancer diagnosis to enrollment was 29 months, and 93.4% had stage I or II disease. Among 497 women who were followed for pregnancy status, 368 (74.0%) had at least one pregnancy and 317 (63.8%) had at least one live birth. In total, 365 babies were born. At 1638 patient-years of follow-up (median follow-up, 41 months), 44 patients had a breast cancer event, a result that did not exceed the safety threshold. The 3-year incidence of breast cancer events was 8.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.3 to 11.6) in the treatment-interruption group and 9.2% (95% CI, 7.6 to 10.8) in the control cohort.
Conclusions: Among select women with previous hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer, temporary interruption of endocrine therapy to attempt pregnancy did not confer a greater short-term risk of breast cancer events, including distant recurrence, than that in the external control cohort. Further follow-up is critical to inform longer-term safety. (Funded by ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation and others; POSITIVE ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02308085.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Women with Breast Cancer Can Attempt Pregnancy.Cancer Discov. 2023 Jul 7;13(7):1504-1505. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2023-0039. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 37199496
-
Pregnancy wishes after breast cancer-an unsettled conflict solved?Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 30;12(11):2976-2978. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1435. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38130301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sopik V International variation in breast cancer incidence and mortality in young women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2021; 186: 497–507. - PubMed
-
- Ruggeri M, Pagan E, Bagnardi V, et al. Fertility concerns, preservation strategies and quality of life in young women with breast cancer: baseline results from an ongoing prospective cohort study in selected European centers. Breast 2019;4 7: 85–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
