In vitro activities of omadacycline, eravacycline, cefiderocol, apramycin, and comparator antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii causing bloodstream infections in Greece, 2020-2021: a multicenter study
- PMID: 37133639
- PMCID: PMC10155660
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-023-04616-7
In vitro activities of omadacycline, eravacycline, cefiderocol, apramycin, and comparator antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii causing bloodstream infections in Greece, 2020-2021: a multicenter study
Abstract
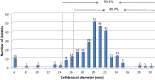
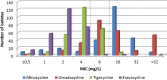
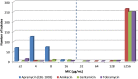
Resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii to multiple clinically important antimicrobials has increased to very high rates in Greece, rendering most of them obsolete. The aim of this study was to determine the molecular epidemiology and susceptibilities of A. baumannii isolates collected from different hospitals across Greece. Single-patient A. baumannii strains isolated from blood cultures (n = 271), from 19 hospitals, in a 6-month period (November 2020-April 2021) were subjected to minimum inhibitory concentration determination and molecular testing for carbapenemase, 16S rRNA methyltransferase and mcr gene detection and epidemiological evaluation. 98.9% of all isolates produced carbapenemase OXA-23. The vast majority (91.8%) of OXA-23 producers harbored the armA and were assigned mainly (94.3%) to sequence group G1, corresponding to IC II. Apramycin (EBL-1003) was the most active agent inhibiting 100% of the isolates at ≤16 mg/L, followed by cefiderocol which was active against at least 86% of them. Minocycline, colistin and ampicillin-sulbactam exhibited only sparse activity (S <19%), while eravacycline was 8- and 2-fold more active than minocycline and tigecycline respectively, by comparison of their MIC50/90 values. OXA-23-ArmA producing A. baumannii of international clone II appears to be the prevailing epidemiological type of this organism in Greece. Cefiderocol could provide a useful alternative for difficult to treat Gram-negative infections, while apramycin (EBL-1003), the structurally unique aminoglycoside currently in clinical development, may represent a highly promising agent against multi-drug resistant A. baumanni infections, due to its high susceptibility rates and low toxicity.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Apramycin; ArmA; Cefiderocol; Eravacycline; IC II; OXA-23.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissemination of International Clone II Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Coproducing OXA-23 Carbapenemase and 16S rRNA Methylase ArmA in Athens, Greece.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Jan;26(1):9-13. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2019.0075. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 31393211
-
In vitro activity of apramycin (EBL-1003) in combination with colistin, meropenem, minocycline or sulbactam against XDR/PDR Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Greece.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024 May 2;79(5):1101-1108. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae077. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38501368 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of cefiderocol, cefepime/enmetazobactam, cefepime/zidebactam, eravacycline, omadacycline, and other comparative agents against carbapenem-non-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii isolates associated from bloodstream infection in Taiwan between 2018-2020.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022 Oct;55(5):888-895. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.08.012. Epub 2021 Sep 4. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022. PMID: 34521591
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
-
Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Greece: an extended review (2000-2015).Future Microbiol. 2017 Jul;12:801-815. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0200. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Future Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28604100 Review.
Cited by
-
Laboratory Surveillance of Acinetobacter spp. Bloodstream Infections in a Tertiary University Hospital during a 9-Year Period.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 19;8(11):503. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8110503. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37999622 Free PMC article.
-
From Clinical Trials to Real-World Experiences: Evidence About Cefiderocol Use and Potential Role in Empirical Therapy.Infect Dis Ther. 2025 May;14(5):897-909. doi: 10.1007/s40121-025-01147-w. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Infect Dis Ther. 2025. PMID: 40205143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of the Genetic Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Tertiary Greek Hospital.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 5;15(4):458. doi: 10.3390/genes15040458. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674392 Free PMC article.
-
Current Therapeutic Approaches for Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 15;13(3):261. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030261. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future approach for the management of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 1;38(2):128-135. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000001092. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39831591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kinross P, Gagliotti C, Merk H, Plachouras D, Monnet DL, Högberg LD, EARS-Net Study Group; EARS-Net Study Group participants Large increase in bloodstream infections with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter species during the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic, EU/EEA, 2020 and 2021. Euro Surveill. 2022;27:2200845. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.46.2200845. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

