Efficacy of Roflumilast Foam, 0.3%, in Patients With Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Double-blind, Vehicle-Controlled Phase 2a Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37133856
- PMCID: PMC10157502
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.0846
Efficacy of Roflumilast Foam, 0.3%, in Patients With Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Double-blind, Vehicle-Controlled Phase 2a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Current topical treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis are limited by efficacy and/or safety.
Objective: To assess safety and efficacy of roflumilast foam, 0.3%, in adult patients with seborrheic dermatitis affecting the scalp, face, and/or trunk.
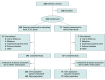
Design, setting, and participants: This multicenter (24 sites in the US and Canada) phase 2a, parallel group, double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical trial was conducted between November 12, 2019, and August 21, 2020. Participants were adult (aged ≥18 years) patients with a clinical diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis for a 3-month or longer duration and Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 3 or greater (at least moderate), affecting 20% or less body surface area, including scalp, face, trunk, and/or intertriginous areas. Data analysis was performed from September to October 2020.
Interventions: Once-daily roflumilast foam, 0.3% (n = 154), or vehicle foam (n = 72) for 8 weeks.
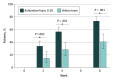
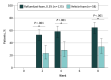
Main outcomes and measures: The main outcome was IGA success, defined as achievement of IGA score of clear or almost clear plus 2-grade improvement from baseline, at week 8. Secondary outcomes included IGA success at weeks 2 and 4; achievement of erythema score of 0 or 1 plus 2-grade improvement from baseline at weeks 2, 4, and 8; achievement of scaling score of 0 or 1 plus 2-grade improvement from baseline at weeks 2, 4, and 8; change in Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score from baseline; and WI-NRS success, defined as achievement of 4-point or greater WI-NRS score improvement in patients with baseline WI-NRS score of 4 or greater. Safety and tolerability were also assessed.
Results: A total of 226 patients (mean [SD] age, 44.9 [16.8] years; 116 men, 110 women) were randomized to roflumilast foam (n = 154) or vehicle foam (n = 72). At week 8, 104 (73.8%) roflumilast-treated patients achieved IGA success compared with 27 (40.9%) in the vehicle group (P < .001). Roflumilast-treated patients had statistically significantly higher rates of IGA success vs vehicle at week 2, the first time point assessed. Mean (SD) reductions (improvements) on the WI-NRS at week 8 were 59.3% (52.5%) vs 36.6% (42.2%) in the roflumilast and vehicle groups, respectively (P < .001). Roflumilast was well tolerated, with the rate of adverse events similar to that of the vehicle foam.
Conclusions and relevance: The results from this phase 2a randomized clinical trial of once-daily roflumilast foam, 0.3%, demonstrated favorable efficacy, safety, and local tolerability in the treatment of erythema, scaling, and itch caused by seborrheic dermatitis, supporting further investigation as a nonsteroidal topical treatment.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04091646.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tucker D, Masood S. Seborrheic dermatitis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

