Protocol to assess fatal embolism risks from human stem cells
- PMID: 37133989
- PMCID: PMC10176070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102268
Protocol to assess fatal embolism risks from human stem cells
Abstract
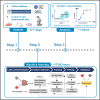
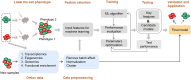
Here, we present a protocol to identify the pro-embolic sub-population of human adipose-derived multipotent stromal cells (ADSCs) and predict fatal embolism risks from ADSC infusion. We describe steps for the collection, processing, and classification of ADSC single-cell RNA-seq data. We then detail the development of a mathematical model for predicting ADSC embolic risk. This protocol allows for the development of prediction models to enhance the assessment of cell quality and advance the clinical applications of stem cells. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Yan et al. (2022).1.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Health Sciences; RNAseq; Stem Cells.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic heterogeneity of cultured ADSCs corresponds to embolic risk in the host.iScience. 2022 Aug 4;25(8):104822. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104822. eCollection 2022 Aug 19. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35992088 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol to estimate cell type proportions from bulk RNA-seq using DAISM-DNNXMBD.STAR Protoc. 2022 Jul 31;3(3):101587. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101587. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. STAR Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35942344 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for fast scRNA-seq raw data processing using scKB and non-arbitrary quality control with COPILOT.STAR Protoc. 2022 Dec 16;3(4):101729. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101729. Epub 2022 Sep 30. STAR Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36181683 Free PMC article.
-
Glyoxalase-1 Overexpression Reverses Defective Proangiogenic Function of Diabetic Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice Model of Critical Limb Ischemia.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Jan;6(1):261-271. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0380. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28170200 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of adipose-derived stem cells and collagenase in fat tissue preparation.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013 Aug;37(4):802-8. doi: 10.1007/s00266-013-0156-7. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013. PMID: 23824057
References
-
- Wickham H. Use R! 2nd edn. Springer International Publishing: Imprint; Cham: 2016. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis; p. 1.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

