Strategic and entrepreneurial abilities: Surviving the crisis across countries during the Covid-19 pandemic
- PMID: 37134095
- PMCID: PMC10155951
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285045
Strategic and entrepreneurial abilities: Surviving the crisis across countries during the Covid-19 pandemic
Abstract
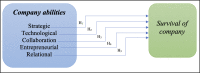
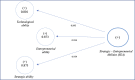
This paper seeks to identify organisational abilities that influence the company's survival during crises. To address this issue, first-through literature review-we identified five groups of crucial organisational abilities that companies pursue during the crisis, i.e., strategic, technological, collaboration, entrepreneurial and relational. We have also identified four objectives that relate to surviving the crisis. Next, we have scrutinised 226 companies from two sides of the world, Poland (Europe) and Morocco (Africa), during the Covid-19 crisis. Quantitative analysis using Structural Equations Modelling demonstrated that surviving during a crisis depends mostly on strategic and entrepreneurial abilities such as the ability to shift resources quickly, organise the work in the firm effectively and plan strategically, as well as diversify its products and services perceived as critical.
Copyright: © 2023 Chudziński et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ESG performance in the time of COVID-19 pandemic: cross-country evidence.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Mar;30(14):39978-39993. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-25050-w. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36600157 Free PMC article.
-
A company's relational strategy: Linkage between strategic choices, attributes, and outcomes.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 22;16(7):e0254531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254531. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34293001 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Network Relations in Poland during the Economic Crisis Caused by COVID-19: Interorganizational Network Viewpoints.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 9;20(2):1178. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021178. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673933 Free PMC article.
-
The COVID-19 pandemic and the role of responsible leadership in health care: thinking beyond employee well-being and organisational sustainability.Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). 2021 Feb 8;34(1):52-68. doi: 10.1108/LHS-09-2020-0071. Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). 2021. PMID: 33818971 Review.
-
Differences of corruption types in selected Western and central-eastern health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Front Public Health. 2023 Oct 9;11:1269189. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1269189. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37876721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How does company misconduct affect company survival risk?-evidence from China.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 5;19(12):e0306767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306767. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39636833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhaduri RM. Leveraging culture and leadership in crisis management. Eur J Train Dev. 2019;43: 554–569. doi: 10.1108/EJTD-10-2018-0109 - DOI
-
- Haddon A, Loughlin C, McNally C. Leadership in a time of financial crisis: What do we want from our leaders? Leadersh Organ Dev J. 2015;36: 612–627. doi: 10.1108/LODJ-12-2013-0166 - DOI
-
- Leung P, Lam T. Crisis Management During the SARS Threat. A Case Study of the Metropole Hotel in Hong Kong. J Hum Resour Hosp Tour. 2004;3: 47–57. 10.1300/J171v03n01_05 - DOI
-
- Pounder P. Responsible leadership and COVID-19: small Island making big waves in cruise tourism. Int J Public Leadersh. 2021;17: 118–131. doi: 10.1108/IJPL-08-2020-0085 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical