Functional modular networks identify the pivotal genes associated with morphine addiction and potential drug therapies
- PMID: 37138216
- PMCID: PMC10155436
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02111-2
Functional modular networks identify the pivotal genes associated with morphine addiction and potential drug therapies
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Functional modular networks identify the pivotal genes associated with morphine addiction and potential drug therapies.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Mar 9;24(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02482-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38459439 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Chronic morphine usage induces lasting molecular and microcellular adaptations in distinct brain areas, resulting in addiction-related behavioural abnormalities, drug-seeking, and relapse. Nonetheless, the mechanisms of action of the genes responsible for morphine addiction have not been exhaustively studied.
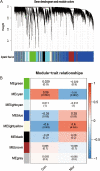
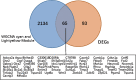
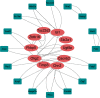
Methods: We obtained morphine addiction-related datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and screened for Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs). Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) functional modularity constructs were analyzed for genes associated with clinical traits. Venn diagrams were filtered for intersecting common DEGs (CDEGs). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis for functional annotation. Protein-protein interaction network (PPI) and CytoHubba were used to screen for hub genes. Potential treatments for morphine addiction were figured out with the help of an online database.
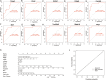
Results: Sixty-five common differential genes linked to morphine addiction were identified, and functional enrichment analysis showed that they were primarily involved in ion channel activity, protein transport, the oxytocin signalling pathway, neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions, and other signalling pathways. Based on the PPI network, ten hub genes (CHN2, OLIG2, UGT8A, CACNB2, TIMP3, FKBP5, ZBTB16, TSC22D3, ISL1, and SLC2A1) were checked. In the data set GSE7762, all of the Area Under Curve (AUC) values for the hub gene Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were greater than 0.8. We also used the DGIdb database to look for eight small-molecule drugs that might be useful for treating morphine addiction.
Conclusions: The hub genes are crucial genes associated with morphine addiction in the mouse striatum. The oxytocin signalling pathway may play a vital role in developing morphine addiction.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Morphine addiction; Opioids; Oxytocin signalling pathway; Weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The database contains samples downloaded from the GEO database (
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Two hub genes of bipolar disorder, a bioinformatics study based on the GEO database.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Jul 21;17:122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.07.006. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39157463 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Inflammation-related Genes as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Sepsis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2023 Jul;29(5):24-31. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023. PMID: 37235492
-
Gene Correlation Network Analysis to Identify Biomarkers of Peri-Implantitis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Aug 19;58(8):1124. doi: 10.3390/medicina58081124. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36013591 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation and imbalance of innate and adaptive immunity are involved in the cardiomyopathy progression.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 6;9:973279. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.973279. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36148059 Free PMC article.
-
Network-Based Data Analysis Reveals Ion Channel-Related Gene Features in COVID-19: A Bioinformatic Approach.Biochem Genet. 2023 Apr;61(2):471-505. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10280-x. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 36104591 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of FKBP5 and its genetic mutations in stress-induced psychiatric disorders: an opportunity for drug discovery.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jun 16;14:1182345. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1182345. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37398599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roy S, Guo X, Kelschenbach J, Liu Y, Loh HH. In vivo activation of a mutant mu-opioid receptor by naltrexone produces a potent analgesic effect but no tolerance: role of mu-receptor activation and delta-receptor blockade in morphine tolerance. J Neurosci. 2005;25(12):3229–3233. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.0332-05.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

